The best bench grinding wheel material depends on what you are working on, why you are grinding, and how smooth you want the finish. The grinding wheel material is very important for how well it works, how safe it is, and how good the final result looks. Research shows that picking the right material changes how well grinding works and how smooth the surface is. This happens because the material changes how heat and force act during grinding. For example, diamond wheels usually make smoother surfaces and cause less heat damage. Aluminum oxide wheels can make more heat and change the stress on the surface.
Key Takeaways
Pick grinding wheel materials by thinking about the metal and the job. This helps you get the best results. Aluminum oxide wheels are good for steel and cast iron. They also do not cost too much for many jobs. Diamond and CBN wheels last longer than others. They make smoother finishes on very hard things like carbide and hardened steel. Always look at wheels for damage before using them. Use the right speed and wear safety gear to stay safe. Use the checklist to choose the right wheel, grit, and bond type. This can help you save money and make your grinding better.
Why Grinding Wheel Material Matters
Performance Impact
The material of a grinding wheel is very important. It affects how well the wheel works. The abrasive type and how it is placed on the wheel matter. These things change how fast you can grind and how long the wheel lasts. If you pick the right abrasive, you can remove metal faster. You also get a smoother finish. Wheels with more holes let coolant move better. They also help chips leave the wheel. This keeps the wheel cool and stops it from wearing out too fast. Dressing the wheel often shows new abrasive grains. This keeps the wheel working well for a longer time. Changing the wheel speed and pressure for each job helps you get good results.
Tip: Wheels with more holes do not clog as much. They last longer because they let chips out and stay cool.
Suitability for Metals
Picking the right grinding wheel depends on the metal you use. Aluminum oxide wheels work well for steel and cast iron. They give a good finish and are reliable. Softer wheels with more holes are better for low carbon steel. Hard wheels can make the grinder shake. Silicon carbide wheels are good for hard alloys and metals like copper. Diamond wheels are best for very hard stuff and coatings. You may need to practice to find the best way to grind and pick the right wheel.
Suitable Metals and Applications | Key Characteristics and Notes | |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum Oxide | Steels, stainless steels, cast iron | Works for many jobs, not expensive, very useful |
Silicon Carbide | Hard alloys, cast iron, non-ferrous metals | Cuts fast, cleans itself, works on sticky coatings |
Diamond | Hardened steels, tungsten carbide | Strongest, removes material fast, makes smooth finish |
Safety Considerations
Using the wrong grinding wheel can be very dangerous. The wheel might break and send pieces flying. This can hurt you. If the wheel gets too hot, it can damage your work and the wheel. Sometimes the wheel can break suddenly. People can get hurt by flying pieces or breathing in dust. Loud noise or shaking means the wheel is not balanced or is broken. This makes it more risky. Picking the right wheel, using the right speed, and using coolant can help keep you safe.
Note: Always make sure the wheel matches the job and material. This helps stop accidents and keeps grinding safe.
Bench Grinding Wheel Materials
Aluminum Oxide
Aluminum oxide is a common abrasive for bench grinding wheels. Makers use brown corundum and white corundum for different jobs. Brown corundum is tough and lasts a long time. It works well for heavy grinding. White corundum is sharper and good for careful grinding. Aluminum oxide wheels are used on steel and cast iron. They are also good for sharpening tools and getting surfaces ready. The grains break during use and show new sharp edges. This keeps the wheel sharp. Wheels come in many grit sizes for rough or smooth work. Aluminum oxide wheels give steady results and do not get too hot.
Property | Brown Corundum | White Corundum |
|---|---|---|
Toughness | High | Medium |
Cutting Ability | Moderate | High |
Typical Use | Heavy grinding | Precision grinding |
Note: Aluminum oxide is a regular abrasive and works well for many shop jobs.
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is another popular wheel material. It has sharp grains and comes in different shapes. Brown and white corundum are not in silicon carbide wheels. Silicon carbide wheels are great for grinding metals that do not have iron, carbide tools, and hard alloys. They cut fast and clean themselves as they work. Wheels with open holes let heat out and are good for soft materials. Closed wheels are strong and make smooth finishes on hard stuff. Silicon carbide wheels are used for tough grinding, finishing, and sharpening tools. People pick grit size for the finish and how much material they want to remove.
Silicon carbide wheels work on copper and carbide.
They are good for both rough and smooth jobs.
Safety and using the right machine are important for best results.
Diamond
Diamond wheels are superabrasives. They use diamond, which is the hardest material. Diamond wheels grind carbide, ceramics, stone, and other very hard things. The wheel has diamond parts held by metal, resin, or glass-like bonds. The shape and hardness of the bond change how the wheel works. Coarse grits take off material fast. Fine grits make smooth surfaces. Diamond wheels are used for gashing, shaping, burr grinding, and finishing. They are also great for sharpening saws and shaping tools. Diamond wheels keep their shape and are very exact.
Diamond wheels work on very hard materials.
They last a long time and give steady results.
CBN
Cubic boron nitride, or CBN, is another superabrasive. CBN wheels grind hard metals like tool steel and cast iron. CBN is very hard, just under diamond. These wheels last longer than regular abrasives and do not wear out fast. CBN wheels let heat out well and protect sensitive materials from damage. They stay sharp and grind very exactly. Factories use CBN wheels for jobs that need high accuracy. CBN wheels save money because they last long and need less changing.
CBN wheels are good for hard steels.
They make surfaces smoother and help grind faster.
Bond Types
The bond in a grinding wheel holds the grains together. Vitrified bonds are strong and handle heat, so they are good for most grinding and removing lots of material. Resin bonds bend and take hits but do not last as long. Metal bonds are very tough and let the wheel sharpen itself, so it lasts longer. The bond you pick changes how hard the wheel is, how it handles heat, and how it cuts. Picking the right bond for your job and material helps the wheel work best and last longer.
Tip: You can dress metal-bonded wheels to show new sharp grains and keep them cutting well.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Aluminum Oxide – Advantages
Aluminum oxide wheels can be used for many jobs. They work well on steel and cast iron. These wheels cut fast and make smooth surfaces. They do not cost much, so they save money. The grains break and show new sharp edges. This helps the wheel last longer. If you use and care for them right, they can last a short or long time. Many people think aluminum oxide wheels are easy to clean and fix.
Aluminum oxide wheels are liked by many because they work well and do not cost a lot.
Aluminum Oxide – Disadvantages
These wheels wear out faster on hard metals. This makes them not last as long. Aluminum oxide wheels are not great for fast or careful grinding. They make more heat when grinding hard. This can hurt the metal and the wheel. Some wheels last only 30 minutes to 2 hours. You may need to buy new wheels more often than CBN or diamond wheels. They do not work well on very hard or breakable stuff. Aluminum oxide wheels can get blocked if used on soft metals.
Silicon Carbide – Advantages
Silicon carbide wheels are very hard and strong. They keep sharp edges for a long time. They let heat out fast, so things do not get too hot. These wheels work well at high speeds and in tough places. They are good for grinding hard and breakable things like glass. Silicon carbide wheels do not get blocked easily. They keep cutting well. People do not need to change these wheels often.
Silicon carbide wheels are tough and do not get hot easily. They are good for hard jobs.
Silicon Carbide – Disadvantages
Silicon carbide wheels can break or chip because they are brittle. They do not work well on steel or iron. People use them more for making things smooth than for hard grinding. They do not keep their edge on tough metals. Sometimes, they need to be mixed with other abrasives for steel. These wheels wear out fast if used wrong. Their brittleness makes them less useful for some jobs.
Diamond – Advantages
Diamond wheels are very hard and last a long time. They work better than other wheels on hard things. Diamond wheels keep their shape and cut well even when hot. They make less friction and heat, so they last longer. Diamond wheels cut clean and make smooth surfaces. They let heat out fast, so the wheel and metal stay safe. Diamond wheels are best for grinding carbide, glass, and ceramics.
Diamond wheels cut very well and last a long time when used on hard things.
Diamond – Disadvantages
Diamond wheels do not work on steel because of chemical changes. Steel dust can hurt the wheel and make it wear out fast. Grinding steel fast can make the wheel break down more. Diamond wheels are hard to shape and need special tools. They are not flexible, so they can wear unevenly. These wheels do not cool steel well, which can cause damage. Do not use diamond wheels on steel or iron.
CBN – Advantages
CBN wheels are made for grinding hard steel and iron. They last much longer than regular wheels. CBN wheels stay sharp and grind very exactly. They help grind faster and make smoother surfaces. CBN wheels let heat out well and protect the metal. They cost more at first, but last longer and save money. Factories change wheels less and work faster with CBN wheels.
CBN wheels work very well and last a long time when grinding steel and iron.
CBN – Disadvantages
Compatibility Drawbacks | Maintenance Drawbacks | |
|---|---|---|
Resin Bond | Gets soft if too hot, so not good for hot jobs | Needs coolant or it gets weak and does not last long |
Hybrid Bond | Needs strong machines, so not for all grinders | Hard to make; needs special tools to clean and fix |
Metal Bond | Not good for many jobs, only some uses | Hard to clean and fix; needs special tools; costs more |
Electroplated & Vacuum Brazed | Cannot be cleaned and fixed, so must buy new ones; costs more | Cuts hard and gets hot; needs coolant to stay safe |
Vitrified Bond | Can crack and break easily | Must be handled with care; needs special tools to fix |
CBN wheels cost much more than regular wheels. You must be careful when you use and store them. Coolant is needed to keep them working well. Some CBN wheels need strong machines or special tools. Taking care of them and using them can cost more. Not all CBN wheels work for every job. You pay more at first, but save money later because they last longer.
Grinding Wheel Selection Guide

For Sharpening Tools
Picking the right grinding wheel keeps tool edges sharp and safe. Aluminum oxide wheels are good for sharpening tools made from carbon steel or hard steel alloys. Ceramic aluminum oxide wheels cut faster and stay cooler. This helps stop heat damage to hard steel alloys. Silicon carbide wheels work well on softer metals like aluminum and cast iron. They can also sharpen carbide-tipped tools. Zirconia alumina wheels remove material quickly and last a long time. They are good for rough sharpening. CBN wheels are best for hard steel alloys and carbide tools. They cost more and need careful handling.
Aluminum oxide: Good for carbon steel and tool steels.
Ceramic aluminum oxide: Best for hard steel alloys, cooler cutting.
Silicon carbide: Works on non-ferrous metals and carbide.
Zirconia alumina: Fast stock removal, long service life.
CBN: For hard steels and carbide, higher cost.
Tip: Pick the right grit size like 60, 80, or 120 for sharpening. Dress and balance the wheel often. This keeps it working well and stops heat damage.
For Shaping and Heavy Grinding
Heavy grinding and shaping need wheels that cut fast and last long. Zirconia alumina wheels are fast and tough. They are great for grinding steel and stainless steel. Ceramic alumina blends are very hard and resist wear. They help shape tough materials. Resin bonds absorb shock and help with high stock removal. Aluminum oxide wheels also work for heavy grinding, especially on steels. To pick the best wheel for shaping, look for hardness, toughness, and cutting speed.
Zirconia alumina: Fast, durable, good for heavy grinding.
Ceramic alumina: Hard, resists wear, cool cutting.
Aluminum oxide: Reliable for steel and heavy-duty jobs.
Resin bonds: Absorb shock, good for vibration-heavy grinding.
Note: Wheels that last longer save money over time. Always check the wheel for cracks or damage before you use it to stay safe.
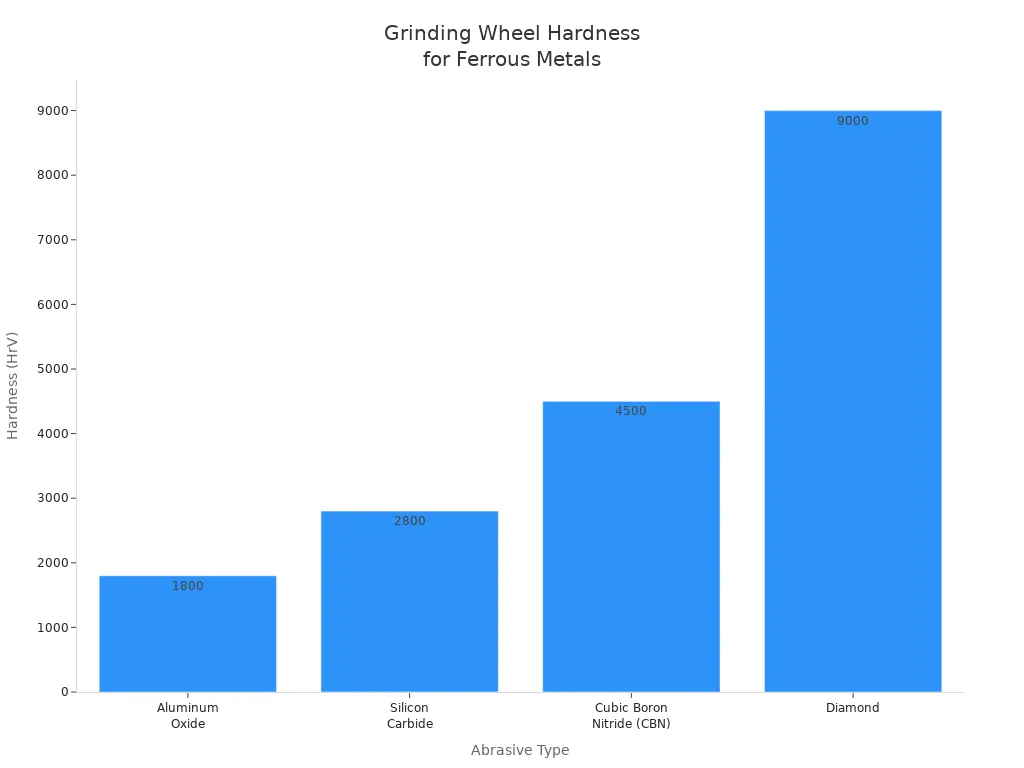
For Steel and Ferrous Metals
Grinding steel and other ferrous metals needs a wheel that is stable and hard. Aluminum oxide wheels are the most common choice for these metals. They work well because they do not react with carbon in steel. CBN wheels are even harder and last much longer. They are great for high-speed steel, hardened cast iron, and tool steels. Ceramic alumina and zirconia alumina wheels also work well, especially for stainless steel and strong alloys. Diamond wheels should not be used on steel. They wear out quickly because of chemical reactions.
Abrasive Type | Suitable Materials and Notes | |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum Oxide | 1800 | Used for grinding ferrous metals; stable with carbon-containing materials |
CBN | 4500 | Great for ferrous metals like high-speed steel, hardened cast iron, tool steel, stainless steel |
Silicon Carbide | 2800 | Used for hard things like glass, ceramics, and non-ferrous metals; not good for ferrous metals |
Diamond | 9000 | Best for non-ferrous and very hard materials; not for ferrous metals |
Safety: Always use the right speed and check the wheel for damage. Using the wrong wheel can cause accidents.
For Carbide and Hard Materials
Grinding tough materials like carbide needs a special wheel. Diamond wheels are the best for carbide and other very hard, brittle materials. They cut clean and last a long time. CBN wheels work well for hardened tool steels and high-alloy steels. They are good for high-production jobs. Silicon carbide wheels can do rough grinding of tungsten carbide. They are not as tough as diamond or CBN. Ceramic alumina wheels help with hard-to-grind metals. They give cooler grinding and last a long time.
Grinding Wheel Material | Characteristics & Benefits | Recommended Use for Hard Materials |
|---|---|---|
Diamond | Best for carbide; extremely hard and sharp | Carbide and other very hard, brittle materials |
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) | Expensive, needs experience; good for high alloy, carburized steels, hardened steels | Hardened tool steels like D2, high production grinding |
Silicon Carbide | Very hard and sharp but brittle; not tough; used mainly for nonferrous and some stainless | Rough grinding of tungsten carbide and brittle hard materials |
Ceramic Alumina | Self-sharpening, cooler grinding, long life; less heat discoloration | Hard-to-grind metals like tool steel, stainless steel |
Tip: Diamond wheels give the best results for carbide. Use coolant to keep the wheel and workpiece cool. This helps the wheel last longer.
For Fine Finishing
Fine finishing needs a wheel that gives a smooth surface and keeps the workpiece safe. Aluminum oxide and ceramic alumina wheels work well for steel and other ferrous metals. They give a good mix of durability and cutting action. Silicon carbide wheels are best for cast iron, non-ferrous metals, and non-metallic materials. They give a sharp cut and even finish. Diamond and CBN wheels work great on hard metals like carbide and hardened steel. Use fine or very fine grit sizes like 70-180 or 200-600 for best results. Closed grain spacing and harder wheel grades help get a finer finish.
Aluminum oxide and ceramic alumina: Best for steel and ferrous metals.
Silicon carbide: Ideal for non-ferrous metals and cast iron.
Diamond and CBN: Excellent for carbide and hardened steel, fine finishes.
Fine and very fine grits: Use for precision and ultra-fine surface finishes.
Note: Always pick the right abrasive type and grit size for the finish you want. Using the right wheel helps stop overheating and keeps your workpiece looking its best.
Quick Reference
Comparison Table
The table below helps you see how different materials change grinding. It shows how hard each is to grind, how much it costs, and how long it takes. This makes it easier to pick the right grinding wheel for your job.
Material Type | Grinding Difficulty & Performance Characteristics | Approximate Cost per Piece (USD) | Estimated Turnaround Time |
|---|---|---|---|
Soft Metals (Aluminum, Brass) | These are easy to grind. You can use lower grit. They work well for small parts and smooth finishes. | 1-3 days | |
Steel | Steel is harder than soft metals. You need higher grit. Stainless steel costs more and takes longer. Polishing adds more time. | $20 – $50 | 3-5 days |
Hard Alloys (Inconel, Titanium) | These are very hard to grind. You need special wheels. They take the most time and cost the most. | $100+ | 5-7+ days |
Plastics | How hard plastics are to grind depends on the type. Heat can cause problems. You might need extra steps for a smooth finish. | $15 – $40 | 2-4 days |
Note: Harder materials usually need pricier wheels. They also take more time to finish.
Selection Checklist
Follow this checklist to help you pick the best grinding wheel:
Find out what material you will grind.
Decide if you want to sharpen, shape, or finish.
Look for wheels that work with your material and job.
Check the price and how long each option takes.
Choose the right grit for the finish you want.
Make sure the wheel fits your grinder and speed.
Look for cracks or damage before you use the wheel.
Always wear goggles and gloves for safety.
Tip: Go over this checklist before you start grinding. It helps you avoid mistakes and keeps you safe.
Picking the right bench grinding wheel material makes your workshop safer and saves money. When workers use the right wheel for each job, they stop the wheel from breaking or getting dirty. This also helps the wheel last longer and means you do not have to stop work as much. The quick reference table lets you see and compare grit, hardness, and what each wheel is good for. If you dress the wheel often and cool it the right way, the wheel will work better and stay safe.
Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Application Type | Matches wheel to job |
Wheel Grit/Hardness | Balances cutting and heat |
Safety Precautions | Prevents injuries and hazards |
Cooling Methods | Protects parts from overheating |
Always check the checklist before you start grinding. This keeps you safe and helps you get the best results.
FAQ
What grinding wheel material works best for sharpening steel tools?
Aluminum oxide wheels sharpen steel tools well. They cut clean and last long. Many shops use them for chisels, knives, and drill bits. CBN wheels also sharpen hard steel but cost more.
Tip: Pick a medium grit for sharper edges.
Can diamond wheels grind regular steel?
Diamond wheels do not work well on regular steel. Steel reacts with diamond and wears the wheel out fast. Use diamond wheels for carbide, glass, or ceramics instead.
Material | Recommended Wheel |
|---|---|
Steel | Aluminum Oxide |
Carbide | Diamond |
How often should someone dress a grinding wheel?
Dressing keeps the wheel sharp and safe. Workers should dress the wheel when it gets clogged or loses shape. For busy shops, dressing once a week helps keep grinding smooth.
Signs to dress:
Uneven surface
Slow cutting
Clogged grains
What safety gear should people wear when grinding?
People should wear safety goggles, gloves, and ear protection. A dust mask helps protect lungs. Closed-toe shoes and long sleeves keep skin safe from sparks.
Safety first: Always check the wheel for cracks before starting.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools













