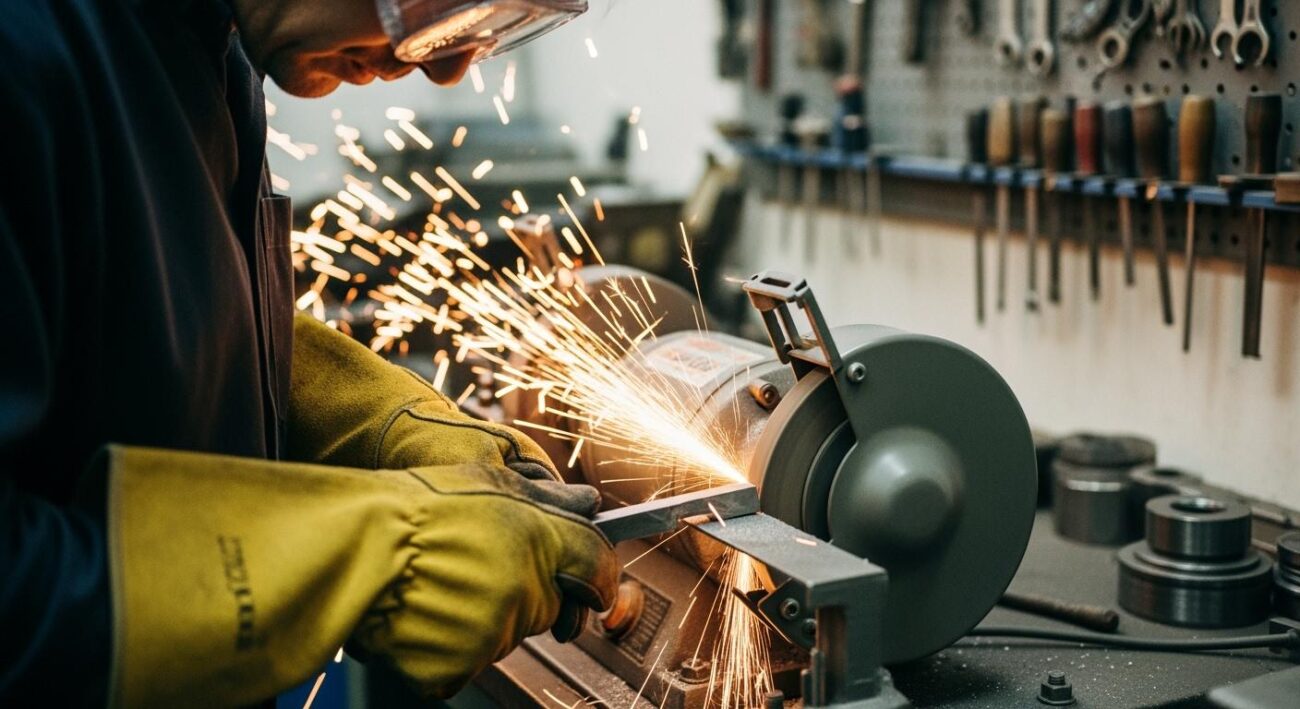
The automotive industry, along with the aerospace and medical sectors, creates the highest industrial demands. These applications require exceptional grinding wheel wear resistance for challenging machining processes. Companies perform precision grinding on difficult materials like superalloys and advanced ceramics.
This type of grinding demands consistent precision with minimal tool wear. The automotive sector, for instance, needs durable tools for its high-volume grinding operations to maintain quality and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- The automotive, aerospace, and medical industries need grinding wheels that last a long time. They work with tough materials.
- Automotive parts like crankshafts and gears need very precise grinding. Strong wheels help make these parts correctly.
- Aerospace parts, such as turbine blades, use special metals. Grinding wheels must be very tough to shape these metals.
- Medical devices, like implants and surgical tools, need perfect surfaces. Grinding wheels must be very precise and clean.
- Tool making and electronics use super hard materials. Diamond grinding wheels are best for these very hard materials.
The Automotive Industry: The Largest Market for Grinding Wheels
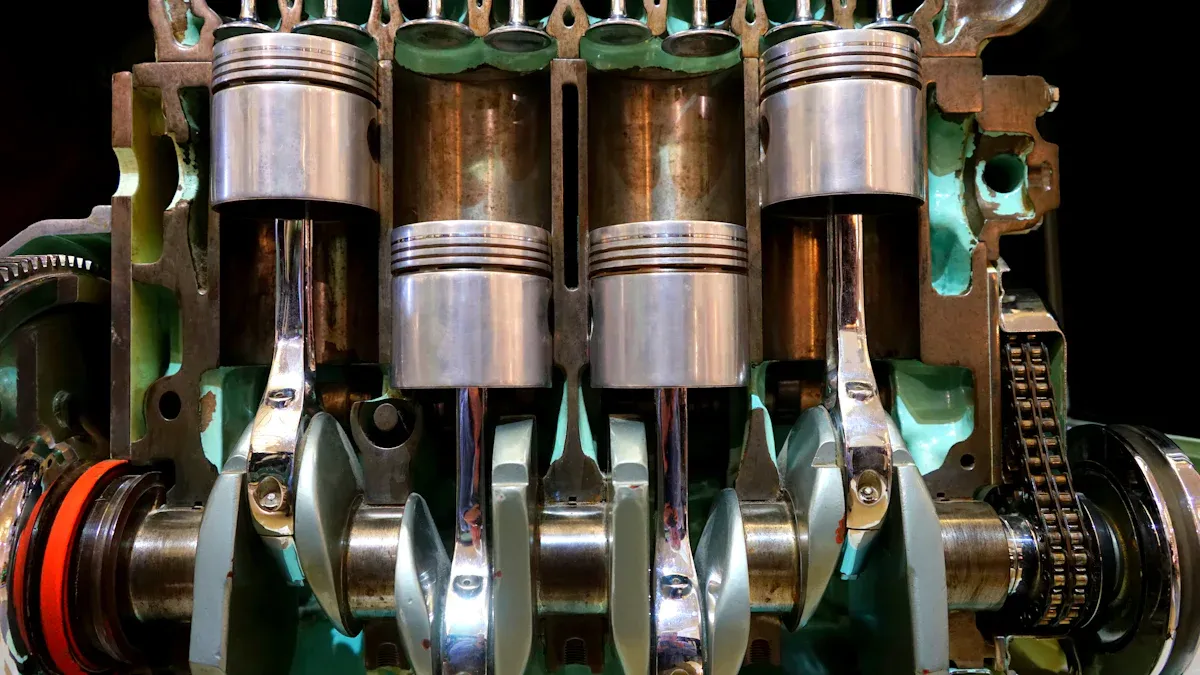
The automotive industry is the largest end-user of grinding wheels, accounting for roughly 35% of total demand. In a mass production environment, wheel longevity and consistent performance are economically critical. The superior durability of a grinding wheel directly lowers the overall cost per part.
Increased wheel life directly translates to producing more parts per wheel and significantly reduces downtime associated with wheel changes, thereby impacting overall cost per part.
This efficiency is vital for reducing costs, as consistent performance minimizes the need for machine adjustments due to wheel wear. Key benefits include:
- Reduced Tooling Costs: Longer-lasting wheels lower the cost per part over time.
- Less Machine Downtime: Better form holding reduces the frequency of wheel changes.
- Improved Part Quality: Durable wheels produce fewer rejected parts, saving material costs.
Crankshaft and Camshaft Grinding
Crankshafts and camshafts are core engine components that require precise grinding. The grinding process shapes lobes and journals to exact specifications. High grinding wheel wear resistance is essential for these applications. Any wear on the wheel can cause dimensional inaccuracies in cam lobe profiles. These inaccuracies directly impact overall engine performance and can even cause operational noise issues.
Precision Machining for Gearbox Components
Transmission gears in the automotive sector demand extreme precision. The grinding of these hardened steel parts must create perfect tooth profiles for smooth and quiet operation. Vitrified cBN abrasives are highly effective for this task. They excel in difficult-to-grind materials and high-volume production where tight tolerances are necessary. This advanced machining ensures high-accuracy gear forms and excellent surface integrity.
Achieving High Grinding Wheel Wear Resistance for Engine Parts
Modern engine components require very close tolerances and superior surface finishes. Grinding is a critical finishing process used to meet these high standards. The continuous wear of a grinding wheel directly influences the surface quality of ground parts. Achieving high wear resistance ensures that every component, from pistons to valves, meets strict quality demands. This level of precision is fundamental to the performance and reliability of today’s automotive vehicles.
The Aerospace Sector: Grinding for Extreme Performance
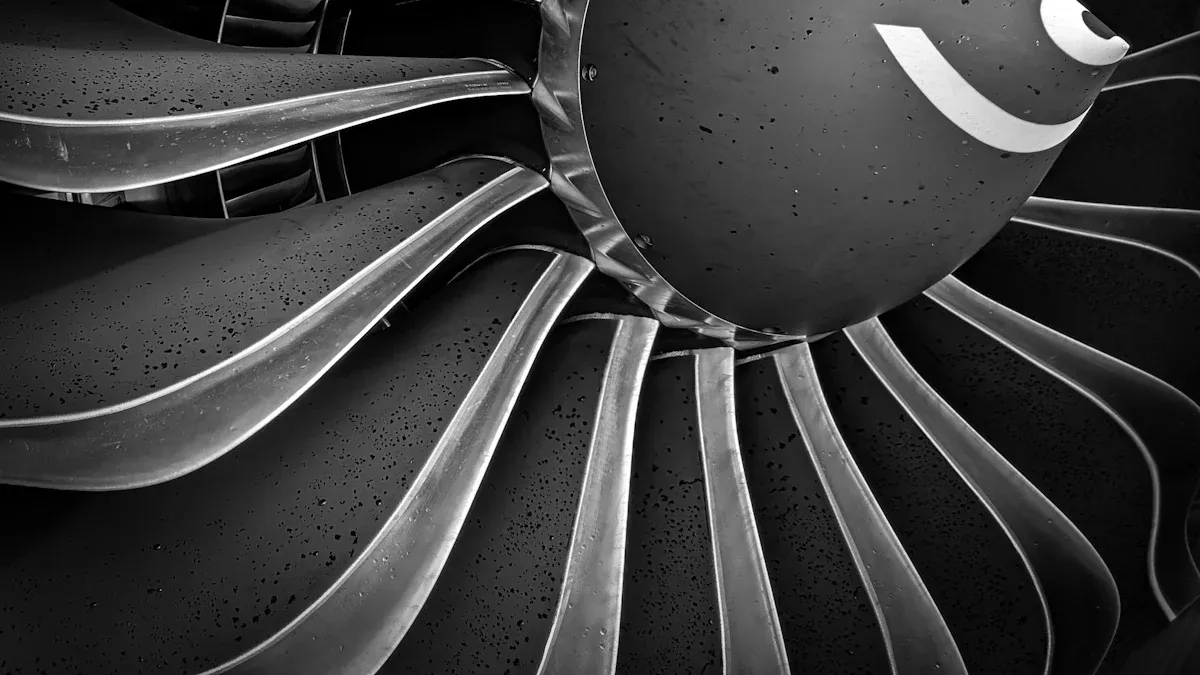

The aerospace industry presents some of the toughest manufacturing challenges. This sector demands extreme precision and reliability for components that operate under intense stress. The grinding of heat-resistant superalloys, such as Inconel and titanium alloys, pushes abrasive technology to its limits. These materials possess high strength at elevated temperatures, making them difficult to machine. To meet these demands, companies need advanced grinding solutions.
Expert Tip: Brands like Aimgrind offer customized formulas and grinding solutions specifically designed for the difficult-to-machine materials common in aerospace applications.
Grinding Turbine Blades and Airfoils
The complex contours of turbine blades and airfoils require flawless geometry. Modern manufacturing uses 5-axis CNC grinding to guide the wheel precisely along these intricate surfaces. This advanced control maintains the perfect orientation between the wheel and the workpiece. Effective coolant application is also critical during the grinding process. It reduces heat, lubricates the cutting zone, and flushes away chips to prevent wheel loading and ensure a superior surface finish.
Machining High-Temperature Superalloys
High-temperature superalloys have poor machinability ratings. Their inherent properties, like high hardness and poor thermal conductivity, create high temperatures at the tool-workpiece interface. This heat can accelerate tool wear and compromise part integrity. Successful machining of these superalloys requires wheels with excellent wear resistance. Hybrid bond and metal bond CBN wheels are highly effective for this type of grinding, offering the durability needed for these tough materials.
Ensuring Form Holding and Thermal Stability
High grinding wheel wear resistance is essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy. A grinding wheel with high thermal stability dissipates heat effectively, preventing surface damage on heat-sensitive aerospace components. Superabrasive wheels made from CBN or diamond generate less friction and maintain their sharp cutting edge longer. This stability reduces the need for wheel dressing, minimizes wear, and extends the tool’s life, ensuring consistent performance.
Creep-Feed Grinding for Complex Geometries
Creep-feed grinding is a highly productive method for creating complex shapes, like the fir-tree roots on turbine blades. This process uses a slow feed rate and a large depth of cut to remove material in a single pass. It offers lower wheel wear and better surface quality compared to traditional grinding methods. This technique is especially economical for processing nickel-based superalloys.
| Process | Parameter | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Creep Feed Grinding | Wheel Speed | 20–30 m/s |
| Grinding Tool Material | Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) | 80–120 mesh grain size |
This method is crucial for parts that need a durable wear and corrosion resistant coating, as it creates a pristine surface ready for finishing.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Uncompromising Precision and Purity
The medical market demands absolute precision and biocompatibility, making grinding a critical manufacturing process. These applications require grinding wheels that deliver flawless surfaces and maintain tight tolerances without introducing contaminants. The need for high wear resistance is paramount when working with advanced, difficult-to-machine materials.
Shaping Orthopedic Implants from Cobalt-Chrome
Manufacturers often shape orthopedic implants from cobalt-chrome, one of the most difficult materials to work with. Its properties present significant challenges for any grinding operation.
Industry experts note that cobalt-chrome’s high hardness, which can have spots reaching 58 HRC, causes rapid tool wear. The material also tends to work-harden during machining, increasing its abrasiveness and dulling cutting edges quickly.
This difficult grinding process requires wheels with exceptional durability to manage the material’s tough nature and ensure consistent production.
Grinding Surgical Instruments and Needles
The production of surgical tools like scalpels, needles, and forceps relies on precision grinding. The goal is to create razor-sharp edges and smooth, defect-free surfaces. Different grinding techniques are used for specific tasks.
| Machining Technique | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| Grinding | Finishing hardened parts, achieving precise tolerances, and polishing surfaces |
For example, resin bond CBN wheels perform the precision sharpening needed for scalpel blades. This specialized grinding ensures every instrument meets strict performance and safety standards.
Critical Surface Finish and Integrity
Surface integrity is non-negotiable for medical devices. The final surface finish can determine an implant’s success. For some orthopedic implants, an optimal surface roughness between 20μm and 25μm helps improve cell attachment. In contrast, articulating joints require a near-mirror finish to reduce friction. The grinding wheel’s characteristics, such as grit size, directly impact this outcome, balancing mechanical abrasion with the final surface quality.
Machining Advanced Biomedical Ceramics
Advanced biomedical ceramics like zirconia and alumina are popular for their durability and biocompatibility. However, their hardness and brittleness make them prone to microcracks during grinding. This challenge demands specialized solutions. Grinding these advanced ceramics often causes excessive wheel wear and long cycle times. Superabrasive grinding wheels with advanced bonds are the solution, as they reduce grinding forces and cut cycle times while extending tool life significantly. This makes the grinding of hard ceramics more efficient and reliable.
Tool Manufacturing and Electronics: The Need for Ultra-Hard Abrasives
The tool manufacturing and electronics industries require grinding extremely hard materials. These include tungsten carbide, Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD), and Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN). The expanding electronics sector, driven by demand for smartphones and microchips, fuels the need for precision manufacturing. This makes the performance of abrasive tools more critical than ever. The grinding process for these materials demands ultra-hard abrasives to achieve the required accuracy and finish.
Grinding Superhard Cutting Tools
Creating ultrahard tools requires a grinding material that is even harder. Diamond is the dominant material for this task, holding a major market share due to its superior hardness and durability. The grinding of these tools is one of the most demanding industrial applications.
For these challenging tasks, Aimgrind’s diamond grinding wheels provide exceptional performance. Their customized formulas ensure efficient material removal and precision when shaping superhard materials, making them a top choice for tool manufacturers. The use of a quality diamond abrasive is essential for this type of grinding.
Sharpening Carbide Saws and Milling Tools
Regular sharpening extends the life of carbide tools and ensures clean, precise cuts. Diamond grinding wheels are the ideal method for this process. Carbide is brittle, so the precision of a diamond abrasive prevents chipping during the grinding operation. Using the correct diamond wheel for the grinding job is crucial. This approach maintains the tool’s original geometry and avoids heat damage. Proper grinding with diamond wheels restores performance with expert precision.
Processing Brittle Electronic Materials
The electronics industry relies on brittle materials like silicon wafers and advanced ceramics. Grinding these components presents significant challenges, including the risk of microcracks and surface damage. The goal is to achieve sub-micron flatness with low and constant grinding force. This high-precision grinding requires abrasives with excellent wear resistance. The superior hardness of diamond makes it perfect for this work. High-quality diamond wheels enable the delicate grinding needed to produce flawless electronic components without defects.
The intense industrial demands of the automotive industry, aerospace, and medical sectors are catalysts for innovation in grinding. The machining of challenging materials like superalloys and ceramics creates these demands. These grinding applications require high grinding wheel wear resistance and superior grinding performance. This pushes the development of advanced solutions like Aimgrind’s custom diamond wheels.
Partnering with an expert for your grinding needs is key. It ensures optimal grinding results, as seen in automotive and aerospace applications where better grinding tools reduce wear. This makes every grinding operation more effective.
FAQ
What is the role of coolant in grinding?
Coolant is essential for effective grinding. The coolant manages heat at the grinding point. A good coolant also lubricates the process. The coolant flushes away chips, and this coolant action prevents wheel loading. Proper coolant application ensures a better surface finish. The coolant is vital.
What are some common grinding processes?
Different grinding processes achieve specific results. For example, creep-feed grinding removes large amounts of material in one pass. In contrast, high-speed reciprocal grinding uses faster movements for finishing. The choice of grinding method depends on the material and desired outcome of the grinding operation.
How do you choose the right wheel for grinding?
Selecting the correct wheel is critical for any grinding job. Factors include the workpiece material, the required surface finish, and the specific grinding operation. A harder material often requires a superabrasive wheel for efficient grinding. Expert advice can simplify the selection for your grinding needs.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools













