Choosing the correct grinding wheel for heavy-duty applications is essential. A superior grinding wheel delivers excellent grinding performance. The success of any grinding application depends on four factors defining all grinding wheels: the abrasive, the bond, the structure, and the shape. The abrasive is key for all grinding. A proper abrasive ensures efficient grinding. The right abrasive and a quality abrasive bond lead to better performance and safety in demanding grinding environments.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing the right grinding wheel means looking at four main parts: the abrasive, the bond, the structure, and the shape. Each part helps the wheel work best for different jobs.
- Abrasive grains like ceramic alumina and zirconia alumina are important. They help the wheel cut well and last a long time, especially for tough metals like steel.
- The bonding system holds the abrasive grains together. Strong bonds, like resinoid or vitrified, make the wheel safe and help it grind precisely or remove a lot of material quickly.
- The wheel’s grade and structure affect how durable it is and how smooth the finish will be. A hard grade and dense structure are good for tough jobs.
- Special wheels with diamond or CBN are best for very hard materials. They last longer and work better than regular wheels for specific, difficult tasks.
Best Types of Grinding Wheels: Abrasive Grains
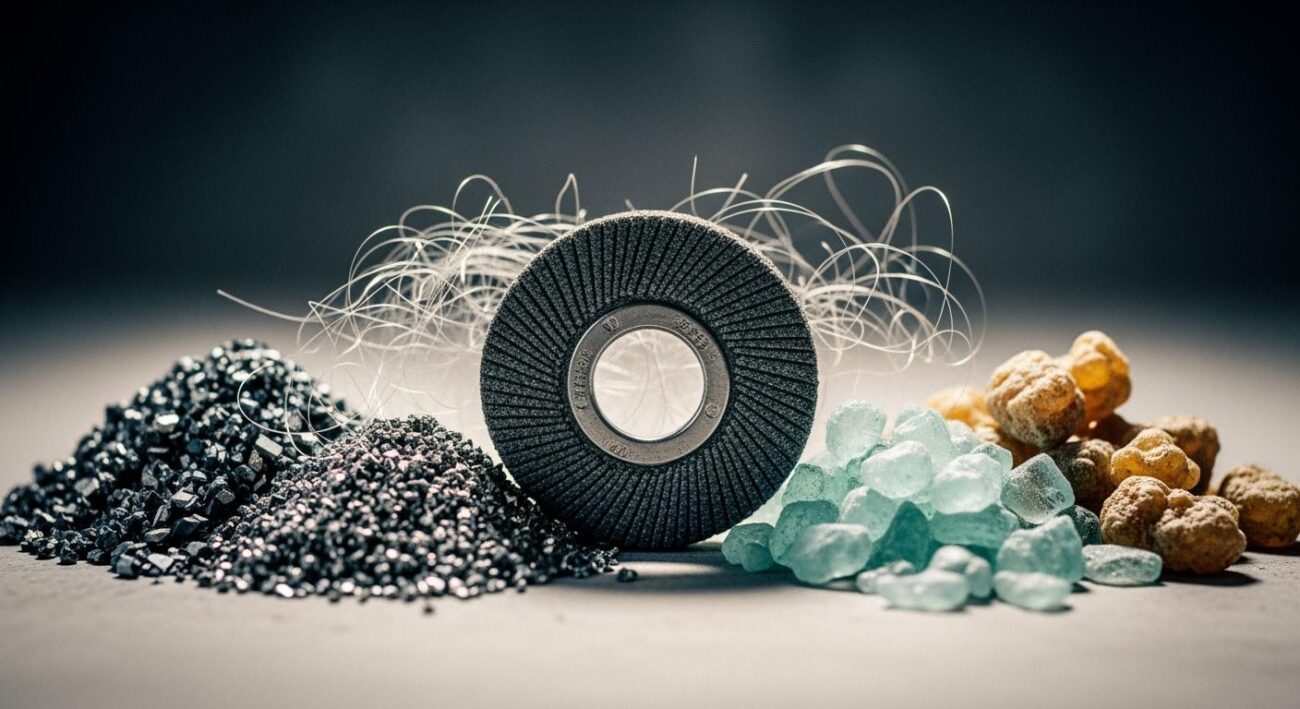
The choice of abrasive grains directly impacts the cutting efficiency and durability of a grinding wheel. The abrasive material performs the actual work of grinding, so selecting the right one is critical for success in heavy-duty steel applications. Specialized providers like Aimgrind help customers select the perfect abrasive formula for specific materials, from hard metals to ceramics. Understanding the best types of grinding wheels starts with the abrasive.
Ceramic Alumina: Cool, Sharp Cutting
Ceramic aluminum oxide is a premium abrasive known for its exceptional hardness and strength. This high-purity grain fractures at a controlled rate during grinding. This action constantly creates new, sharp cutting points.
Key Advantage: Ceramic alumina has high hot hardness. It stays hard even at high temperatures. This property allows for “cool cutting,” which reduces heat buildup on the workpiece surface and can even eliminate the need for liquid coolants in some steel applications.
This makes it a top choice for precision grinding on tough steels and alloys, delivering superior performance.
Zirconia Alumina: The Ideal Grinding Wheel for Steel
Zirconia alumina is a tough, durable abrasive perfect for a grinding wheel for steel. It is a composite material blending aluminum oxide with zirconium dioxide. This combination gives the grinding wheel for steel superior toughness and wear resistance. During grinding, zirconia alumina abrasive grains feature a self-sharpening mechanism. The microcrystalline structure fractures to expose fresh, sharp cutting edges. This process enhances the material removal rate and extends the life of the grinding wheel for steel. Its high bulk density makes it an excellent choice for high-speed and heavy-duty grinding wheels used in demanding steel applications. This is the ideal grinding wheel for steel. The grinding wheel for steel needs this abrasive. A good grinding wheel for steel uses zirconia. The best grinding wheel for steel is often a zirconia alumina wheel.
Coarse Grit Size for Aggressive Stock Removal
The grit size of an abrasive determines the speed of material removal and the quality of the surface finish. For aggressive stock removal, a coarse grit is necessary.
- Lower Grit Numbers (e.g., P24-P80): Indicate larger abrasive particles.
- Faster Material Removal: These large particles cut through material quickly, enabling rapid stock removal.
- Rougher Surface: The trade-off for fast removal is a rougher surface finish.
A coarse grit size is ideal for initial surface preparation steps like removing welds or scale. Operators can achieve high material removal rates, but the resulting surface will require further refinement with a finer grit abrasive. Choosing the best grinding wheel grit depends on balancing speed with the desired surface quality for your steel applications. The grit size is key for performance. A coarse grit is best for fast removal.
The Importance of a Robust Bonding System
The bonding system acts as the backbone of a grinding wheel. It holds the abrasive particles together, defining the wheel’s strength, rigidity, and resistance to heat. The right bond ensures optimal performance and safety during heavy-duty grinding. A proper bond choice directly impacts material removal rates and the final surface quality. Experts at Aimgrind offer a range of bond types, including resin, metal, and vitrified bonded abrasives. This variety allows them to perfectly match the grinding wheel to a customer’s equipment and process requirements for any grinding task.
Resinoid Bonds for Strength and Speed
Resinoid bonds use synthetic resins to hold the abrasive grains. These bonds provide excellent strength and toughness. This makes them ideal for operations that involve high mechanical stress and shock loads. Resinoid bonded abrasives excel at rapid material removal and are a top choice for high speed grinding. Their elasticity allows for a smoother grinding action, which is beneficial for surface preparation.
Note: The maximum operating speed of resinoid grinding wheels varies by design. Wheels with fabric reinforcement can safely reach speeds up to 100 m/s, enabling aggressive stock removal.
Vitrified Bonds for Precision and Rigidity
Vitrified bonds are made from fused clay and ceramic materials. This process creates a very strong, rigid, and porous structure. The high rigidity is key for precision grinding. It allows the grinding wheel to maintain its exact shape, which is critical for creating parts with tight tolerances. This form-holding ability reduces vibration and leads to a superior surface finish.
| Feature | Resinoid Bond | Vitrified Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity | Elastic and tough | High rigidity, brittle |
| Form Holding | Good | Excellent |
| Stock Removal | Ideal for rapid removal | High removal with rigid machines |
| Best Use | High-speed operations, rough grinding | Precision grinding, tight tolerances |
Vitrified wheels are essential in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries for grinding hard materials.
Reinforced Bonds for Operator Safety
Safety is the top priority in any grinding operation. Reinforced bonds add a crucial layer of protection. These grinding wheels incorporate layers of high-tensile materials like fiberglass. This reinforcement dramatically increases the wheel’s structural integrity. It helps the wheel withstand the immense forces of high-speed grinding and aggressive material removal. The reinforcement prevents catastrophic wheel failure, protecting the operator from potential injury and ensuring a safer work environment during surface preparation and stock removal.
The Right Grinding Wheel Grade and Structure
The grade and structure of a grinding wheel are two distinct but related characteristics that define its grinding performance. Grade refers to the strength of the bond holding the abrasive grit, while structure describes the spacing between each abrasive grit. Selecting the correct combination is vital for efficient material removal and achieving a quality surface. For heavy-duty grinding, a harder grade and denser structure are often preferred to withstand intense operational forces.
Hard Wheel Grade for Superior Grain Retention
The grade of a grinding wheel indicates how tightly the bond holds the abrasive grit. This is measured on a scale from A (softest) to Z (hardest). A hard grade grinding wheel has a very strong bond. This strength prevents the abrasive grit from breaking away too quickly during the grinding process. This superior grain retention extends the life of grinding wheels and ensures consistent material removal.
- Soft Grades (A-H): The bond releases abrasive grit easily. This is good for grinding hard materials.
- Medium Grades (I-P): This grade offers a balance for general grinding tasks.
- Hard Grades (Q-Z): The bond holds the abrasive grit securely. This provides long life, especially for grinding softer materials.
For heavy stock removal, a hard grade ensures the grinding wheel maintains its integrity, leading to effective material removal without rapid wear.
Dense Structure for Durability and Form Holding
The structure of a grinding wheel refers to the density of the abrasive grit. This is rated on a scale from 1 (densest) to 16 (most open). A dense structure means the abrasive grit particles are packed closely together. This configuration is essential for durability and form holding. A dense grinding wheel is less prone to wear and better at maintaining its shape, which is critical for precision grinding and creating a smooth surface.
A dense structure improves the surface finish but can generate more heat during material removal. It is crucial for holding form when grinding tight corners or complex profiles, making it ideal for detailed surface preparation.
This dense packing of abrasive grit provides more cutting points on the wheel’s surface, contributing to a finer finish and controlled material removal. This makes dense structure grinding wheels a reliable choice for tasks requiring both aggressive removal and a high-quality final surface.
Wheel Shapes for Heavy-Duty Grinding

The shape of a grinding wheel dictates how it interacts with the workpiece. Selecting the correct profile is crucial for both efficiency and operator safety in any heavy-duty grinding application. Different shapes provide unique advantages for specific tasks, from flat surface grinding to intricate angle work. The right shape ensures optimal contact with the work surface, leading to better control and superior results.
Type 27 Depressed Center Wheels
Type 27 wheels feature a depressed center hub. This design allows the locking nut to sit below the grinding surface. This feature enables operators to perform flush grinding without the fastener interfering with the workpiece. These grinding wheels are extremely versatile for right-angle grinding tasks. Their shape makes them ideal for:
- Weld grinding and beveling
- Snagging and heavy stock removal
- Surface preparation on metal, stainless steel, and concrete
This versatility makes the Type 27 grinding wheel a staple in fabrication shops and construction sites where aggressive grinding is common.
Type 1 Straight Wheels
The Type 1 grinding wheel has a simple, flat profile. It is one of the most common shapes and is often used on bench or pedestal grinders. This wheel is excellent for grinding off excess metal from a workpiece. Its straight edge is perfect for sharpening tools and performing various grinding tasks on flat surfaces, edges, and angles. The flat grinding surface provides consistent contact, making it a reliable choice for general-purpose workshop grinding.
Thicker Profiles for Stability
The thickness of a grinding wheel directly impacts its stability and durability. For heavy-duty grinding, a thicker wheel profile is often necessary. Thicker grinding wheels offer greater lateral strength. This strength helps the wheel resist side-loading pressures and reduces vibration during aggressive material removal.
Pro Tip: A thicker wheel provides a larger grinding surface, which can improve the removal rate and extend the wheel’s life. This enhanced stability improves operator control, boosts performance, and ensures a safer grinding experience.
Advanced Grinding Wheels: Diamond and CBN

When conventional abrasives reach their limits, superabrasives provide the next level of performance for the most demanding grinding applications. These advanced materials, Diamond and Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), deliver unmatched hardness and thermal conductivity. This makes superabrasive wheels essential for high-tolerance work on the toughest materials. The proper selection of superabrasive wheels can reduce overall grinding costs by 25-45% through enhanced productivity.
Diamond Grinding Wheels for Hard Alloys
Diamond is the hardest known material, making it the ultimate choice for grinding extremely hard, non-ferrous materials. Diamond grinding wheels excel at grinding materials where precision is non-negotiable.
- Hard ceramics like Zirconia and Alumina
- Tungsten carbide
- Composites and stone
- Aerospace components
Premium Solution: Aimgrind’s diamond grinding wheels deliver exceptional durability and a long service life. They offer a 300-500% improvement in wheel life over conventional wheels. This makes them a premium solution for precision grinding. Aimgrind’s expertise lies in customizing these advanced wheels. They solve specific customer challenges, enhancing productivity for any grinding application.
CBN Wheels for Ferrous Superalloys
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is the second hardest material after diamond. Its high thermal stability makes it the preferred superabrasive for grinding various steel alloys. Diamond is not suitable for grinding steel because the carbon in the diamond reacts with the iron in the steel at high grinding temperatures. CBN, however, remains stable and maintains sharp cutting edges during the grinding process. This makes it ideal for the high-heat environment of steel grinding. This specific application is where CBN superabrasives truly shine.
CBN is highly effective for grinding:
- High-speed steel
- Tool steel and cast iron
- Heat-resistant superalloys
Choosing between Diamond and CBN depends entirely on the material. Using the correct superabrasive ensures optimal grinding results and cost-efficiency.
Selecting the best wheel involves choosing the right abrasive, a robust bond, a hard grade, and the correct shape. For ultimate performance, advanced solutions like Aimgrind’s diamond wheels offer unparalleled efficiency. While their initial cost is higher, they deliver a lower cost per part by dramatically increasing productivity and tool life. To ensure your wheel is perfectly optimized for safety and productivity, consult with an expert.
Partner with Aimgrind to enhance your operations. Grind with Passion, Achieve with Aim.
FAQ
How do operators select the best grinding wheel for a specific job?
Operators choose a wheel based on four key factors. The abrasive material, bonding system, wheel structure, and shape all determine performance. Matching these characteristics to the specific material and application ensures optimal results and efficiency. Each factor plays a critical role in the grinding process.
What makes a grinding wheel safe for heavy-duty use?
Safety comes from a wheel’s construction. Reinforced bonds with internal fiberglass layers provide structural integrity. This reinforcement prevents wheel failure under high speeds and intense pressure. Proper wheel selection for the job also enhances operator safety and prevents accidents.
When should a user choose a diamond wheel over a conventional one?
A user selects a diamond wheel for grinding extremely hard, non-ferrous materials.
These wheels are essential for tasks requiring high precision on materials like tungsten carbide, hard ceramics, and composites. They offer superior durability and a longer service life for demanding applications.
Why does a hard grade wheel last longer in heavy-duty applications?
A hard grade wheel features a very strong bond. This bond securely holds the abrasive grit, preventing it from breaking away too quickly. This superior grain retention reduces wear during aggressive material removal. The result is a longer-lasting and more durable grinding wheel.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools













