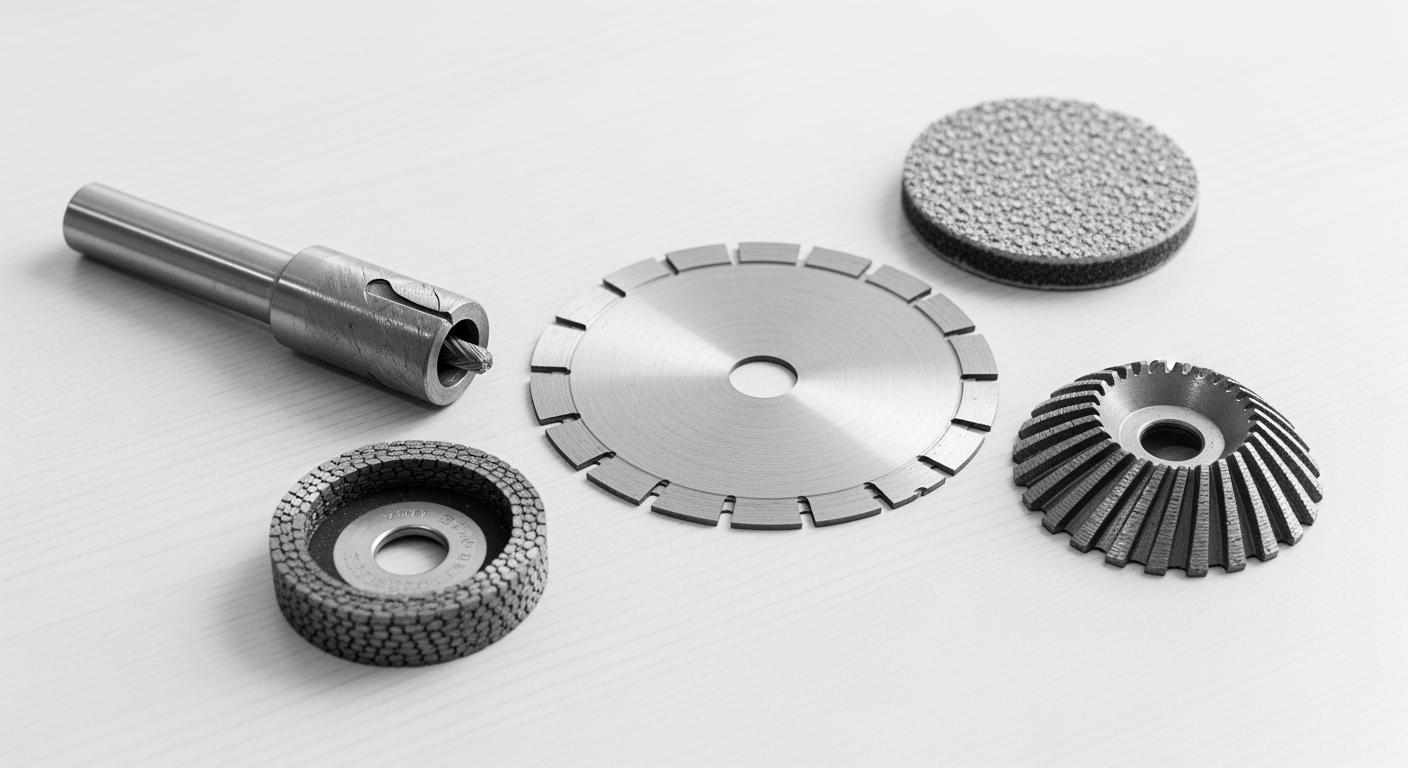
You need the right diamond tools for your job. Your selection depends on three key factors.
- The task you need to perform, such as cutting.
- The material you are working with.
- The final finish you want to achieve.
The market for these tools is growing quickly, projected to reach US$ 23.2 Billion by 2032. This highlights how vital the perfect tool is for various applications. Expert brands like Aimgrind use these core principles to design ideal solutions for you.
Key Takeaways
- Choose your diamond tool based on the job you need to do, like cutting, grinding, or drilling.
- Match the tool’s features, such as diamond size and design, to the material you are working with and the finish you want.
- Use wet drilling for hard materials to make tools last longer and keep dust down.
- High-quality diamonds and strong bonds make tools work better and last longer.
- Aimgrind offers special diamond tools for many jobs, helping you get the best results.
Select Your Tool by Task

Your first step is to match the tool to the job. Different tasks require unique tool designs for the best results. You might need to make a precise cut, smooth a rough surface, or drill a clean hole. Let’s explore the main categories of diamond tooling to help you choose.
Diamond Saws for Precision Cutting
You use diamond saws when your project demands clean, accurate cutting. These powerful cutting tools are essential in many industries. They handle tough materials with ease. Common applications include:
- Cutting stone like granite, marble, and tile
- Slicing through bricks and masonry
- General use in drilling and cutting industries
Pro Tip: The design of your saw blade should match the material’s hardness. A mismatch can lead to poor cuts, chipping, or rapid tool wear.
For example, cutting hard granite is very different from cutting softer marble. You need specific blade features for each job. This table shows how blade design changes based on the material.
| Feature | Granite (Hard Material) | Marble (Softer Material) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | This is the hardest natural stone. It needs strong diamond bonds for durability. | This stone is softer than granite. It needs a smooth blade to prevent chipping. |
| Rim Design | A turbo or segmented rim provides fast, aggressive cuts. | A continuous rim gives a cleaner, chip-free cut. |
| Bonding Material | A harder bond holds the diamonds securely for tough jobs. | A softer bond is better suited for softer stones. |
| Cutting Method | Wet cutting is best. It reduces heat and gives a smoother finish. | You can use dry cutting, but wet cutting gives better results. |
Grinders for Surface Finishing
You need a grinder when your goal is to shape, smooth, or polish a surface. Diamond grinding tools are perfect for preparing or finishing hard materials like concrete. They remove material quickly and create a uniform finish.
Diamond cup wheels are a great example. They improve surface preparation efficiency far more than old-style abrasives. The industrial-grade diamonds on the wheel stay sharp. This allows for rapid material removal on tough concrete floors, saving you time and money on replacements.
When working on concrete floors, you have several types of diamond grinding tools to choose from. Your choice depends on the stage of the project.
- Metal Bond Diamonds: You use these for the initial, aggressive grinding stages.
- Transitional and Hybrid Diamonds: These help you move from coarse grinding to fine polishing.
- Resin Bond Diamonds: You use these for the final polishing steps to get a high-gloss, polished concrete finish.
- Cup Wheels: These come in many designs, like Turbo, Continuous Rim, and Double Row, for specific tasks from rough grinding to fine finishing.
Choosing the right diamond grinding tool involves matching the bond to the surface. A soft bond works best on hard surfaces, while a hard bond is ideal for softer, gritty surfaces.
Drill Bits for Accurate Holes
You select diamond drill bits when you need to create precise, clean holes in very hard materials. These cutting tools are essential for tasks in construction, automotive, and optical industries. They can drill through reinforced concrete, glass, and ceramic without causing cracks.
The specifications for these bits vary widely. This allows you to find the perfect tool for your specific need. For example, bits for drilling hard concrete with steel rebar come in many sizes.
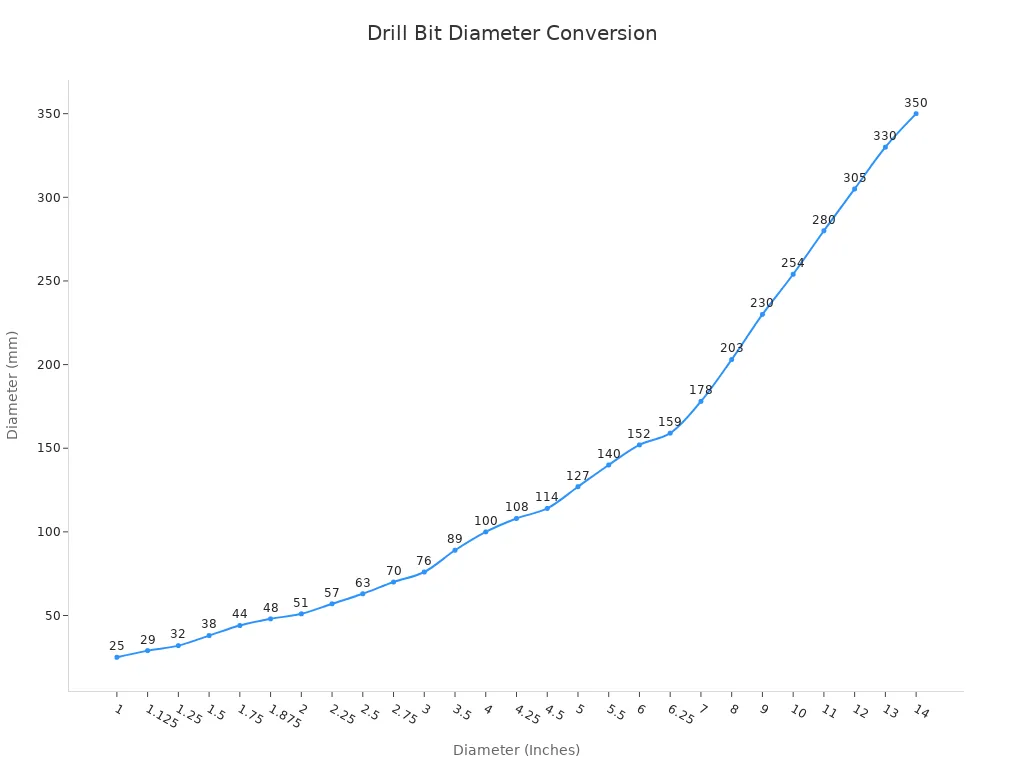
The chart above shows how bit diameters in inches correspond to millimeters. This range ensures you can find a bit for any job, from small anchor holes to large-diameter cores.
You also need to decide between wet and dry drilling. Each method affects the life and performance of your diamond tools. Using water (wet drilling) is often the preferred method for the hardest materials. This table compares the two approaches.
| Feature | Wet Diamond Drilling | Dry Diamond Drilling |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Life | Water extends tool life by reducing heat. | Heat builds up quickly, which can shorten tool life. |
| Efficiency | The coolant flushes away debris for faster cutting. | Debris can slow down the drilling process. |
| Dust Control | Water captures dust, creating a safer workspace. | This method creates significant dust and requires a vacuum. |
| Material Suitability | This is best for hard materials like reinforced concrete. | This works for softer materials or where water is not allowed. |
Understanding these differences helps you protect your investment in diamond tools for grinding and drilling while achieving the best possible results.
Select Features for Material and Finish
After you choose a tool for your task, you need to look at its features. The right features ensure your tool works perfectly on your material and gives you the finish you want. Let’s explore the three most important features: abrasive particle size, tool design, and diamond quality.
Abrasive Particle Size
The size of the diamond particles on your tool is called grit size. This feature directly affects how the tool performs. A different grit size can change your material removal rate and the final surface finish.
Coarse grit diamond tools use larger diamond particles. You should choose them for rapid material removal. They are great for the first steps of a project, like grinding down a rough surface.
| Grit Size | Typical Application |
|---|---|
| 10-24 | Rough grinding, heavy stock removal |
Fine grit tools use smaller diamond particles. You use these for finishing work. For example, polishing steps with 3 µm and then 1 µm diamond abrasives will make a ceramic surface much smoother. The first step with the 3 µm abrasive removes the most roughness.
Aimgrind’s Expertise: For delicate materials like glass or ceramics, getting the particle size right is critical. Aimgrind creates customized solutions that match the diamond particle size to your specific material. This gives you the best possible results without causing damage.
Tool Design and Geometry
The physical design of a diamond tool also plays a big role. The shape of the tool and how the diamonds are attached affect its performance, lifespan, and the type of job it can do. Two common manufacturing methods are sintering and electroplating.
Sintered tools have diamonds mixed into a metal powder. The mixture is heated and pressed, trapping the diamonds inside a metal bond. As you use the tool, the bond wears away and exposes new, sharp diamonds. This design gives the diamond tooling a long life.
Electroplated tools have a single layer of diamonds bonded to the surface. This design exposes more of each diamond, which allows for very aggressive and fast cutting.
The table below compares these two popular designs.
| Feature | Sintered Diamond Tools | Electroplated Diamond Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Diamond Exposure | Diamonds are partially embedded in a bond. | Diamonds are fully exposed on the surface. |
| Cutting Action | Less aggressive; requires more pressure. | More aggressive; offers faster cutting speeds. |
| Tool Life | Generally good as new diamonds are exposed. | Life depends on the single diamond layer. |
| Best For | Grinding hard materials like concrete and stone. | Precision cutting of glass, ceramics, and composites. |
The geometry of a cutting blade also matters. For example, a continuous rim blade provides the smoothest cut on delicate materials like tile and glass. A segmented rim blade offers faster cutting on harder materials like concrete because the gaps help cool the blade and clear debris.
Diamond Material Quality
The quality of the diamonds and the bonding material determines the tool’s durability and performance. A high-quality diamond grinding tool will last longer and work more efficiently.
Aimgrind uses only high-quality diamond grains in its products. These diamonds have superior hardness and wear resistance. This means your tool stays sharp and effective for a longer time. The bond is the material that holds the diamonds in place. The type of metal bond you choose depends on the material you are working on.
- Bronze-based bonds are good for cutting very hard and brittle materials.
- Cobalt-based bonds offer a longer tool life and are great for stone and concrete.
- Steel-based bonds provide a good balance of cutting speed and life for abrasive materials.
Pro Tip: You should always match the bond to the material. A hard bond works best on soft, abrasive materials. A soft bond works best on very hard materials because it wears away to expose new diamonds.
By using durable metal bonds, Aimgrind ensures its diamond tools hold the diamond grains securely. This combination of premium diamonds and strong bonds gives you a reliable tool that performs consistently, project after project.
An Overview of Aimgrind’s Diamond Tools

Choosing the right tool is easier when you partner with a specialist. Aimgrind provides customized abrasive solutions and has deep expertise in diamond tooling for industrial applications. You can find a range of high-performance diamond tools designed to meet specific challenges in your industry.
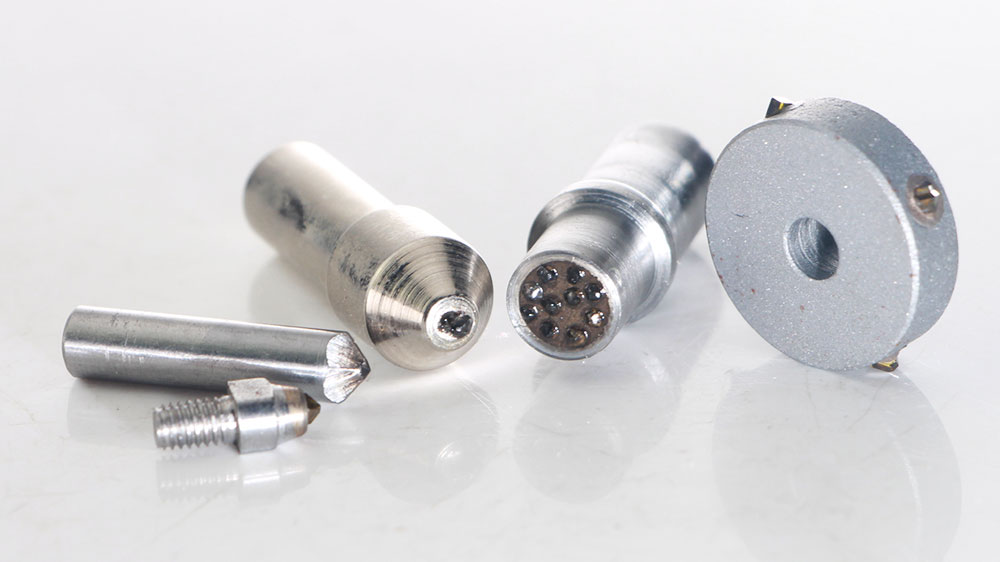
Drill Bits and Countersinks for Glass
You need precision when working with brittle materials like glass. Mechanical drilling often causes cracks and chipping, especially in the automotive and optical industries. Aimgrind’s diamond drill bits are engineered to solve this problem. They create clean, accurate holes without damaging the material.
Pro Tip: To extend tool life and prevent heat fractures in glass, you should use lower drill speeds. For a 1-inch bit, 500 RPM is ideal, while a larger 4-inch bit requires a slower speed of 125 RPM.
These cutting tools give you the control needed for delicate jobs, ensuring a high-quality finish every time.
Milling Cutters and Reamers
For shaping complex surfaces or achieving exact hole diameters, you can turn to milling cutters and reamers.
- Diamond Milling Cutters: You use these for shaping hard materials like composites and ceramics. Their design allows for free cutting, which minimizes delamination and produces an excellent finish.
- Diamond Reamers: When you need micron-level accuracy, a reamer is the right choice. It can achieve a hole tolerance of ±0.005 mm and a surface roughness as fine as Ra 0.2, which is essential for precision components.
These cutting tools deliver superior performance for demanding applications.
Specialized Cutting Tools for Industry
Aimgrind offers specialized cutting tools for a wide range of industries, from aerospace to electronics. These tools are vital for cutting hard matrix composites or slicing silicon wafers for microchips. They provide the high tolerance and smooth surface finish required for these critical jobs. Whether you use CNC machines or manual equipment, you can find versatile diamond tools to fit your process.
Explore the full range of solutions on our diamond tools product page to find the perfect match for your needs.
You can now select the right diamond tools with confidence. First, identify your task. Next, match the tool’s features to your material. Finally, choose a design for your specific applications. Partnering with an expert supplier like Aimgrind ensures you get a high-performance tool perfectly suited to your needs. This choice reduces machine downtime and material waste, lowering your total operational costs.
Ready to find your perfect match? Grind with Passion, Achieve with Aim.
FAQ
What materials can you use diamond tools on?
You should use diamond tools for very hard or brittle materials. They perform exceptionally well on glass, ceramics, stone, and concrete. Their unique hardness allows you to cut these tough materials with precision and minimal damage, ensuring a clean and professional result every time.
Why should you choose diamond tools over conventional ones?
You gain superior durability and efficiency with diamond tools. They last much longer than standard abrasive tools. This longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements. You will save time and lower your long-term operational costs, making them a smart investment for any serious project.
How do you maintain your diamond tools?
You can extend the life of your tools with proper care. Always clean them after each use to remove debris. You should also store them in a dry, safe place to prevent damage. Proper maintenance ensures your tools deliver consistent, high-quality performance for years.
Pro Tip: Use a soft brush and water to gently clean the diamond surface. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the bond holding the diamonds in place.
Can you use Aimgrind diamond tools with CNC machines?
Yes, you can use many Aimgrind diamond tools with CNC machines. Aimgrind designs its tools for versatility. This allows you to integrate them into both automated CNC processes and manual operations. You get precision and efficiency no matter what equipment you use.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools