Choosing the best stainless steel grinding wheel needs you to think about a few things. People want wheels that work fast, make smooth surfaces, cost less, and last longer. Every wheel type has good and bad points for stainless steel. Heat resistance, how hard the wheel is, and grit size matter a lot for how well it works. Grinding stainless steel can cause problems like bending, getting too hot, and tiny cracks. These problems can make the steel weaker or change how it looks. Picking the right stainless steel grinding wheel helps stop heat damage and gives better results.
Key Takeaways
Ceramic alumina and zirconia alumina grinding wheels are best for stainless steel. They last longer and handle heat better than other wheels. Aluminum oxide wheels cost less and work for light or medium jobs. But they wear out faster and can cause heat damage if used too much. Silicon carbide wheels are good for polishing and finishing. They make the surface bright and smooth but wear out fast on hard metals. Picking the right wheel hardness, grit size, shape, and bond type is important. This helps stop heat damage and gives the finish you want on stainless steel. Use light pressure and take breaks while grinding. Choose heat-resistant wheels to stop overheating and keep the steel safe.
Quick Comparison of Grinding Wheels
Types of Abrasives for Stainless Steel
There are many kinds of metal grinding wheels, but not all are good for stainless steel. Some abrasives used for stainless steel are ceramic alumina, aluminum oxide, zirconia alumina, and silicon carbide. Ceramic alumina is very tough and does not get hot easily. Zirconia alumina cuts well and stops heat marks. Aluminum oxide is cheap and easy to find, but it does not last as long as ceramic or zirconia. Silicon carbide cuts fast and makes smooth surfaces, but it wears out quickly.
Grinding wheels for stainless steel should use abrasives that can handle heat and last a long time. Ceramic flap discs are often the best because they work fast and stay cool. Zirconia discs are also good for hard jobs and removing lots of material. Flap wheels and discs help make surfaces smooth and stop heat damage. It is best to use abrasives from rough to fine grit to get a nice finish.
Pros and Cons Overview
The table below shows how each abrasive grinding wheel works on stainless steel:
Abrasive Type | Performance Highlights | Benefits | Drawbacks | Suitability for Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ceramic Alumina | Lasts the longest, cuts fast, has a fine structure, can get hot | Sharpens itself, strong, can be used for many jobs, removes material quickly | Can break if pushed too hard, heat can make it wear out faster | Great for finishing stainless steel and cutting hard materials |
Aluminum Oxide | Most common, not expensive, cuts sharp, gets hot when used | Easy to find, not costly, works on wood, metals, and other things | Makes heat that can hurt the work and the wheel, not good for tough jobs | Good for finishing stainless steel (white aluminum oxide) |
Zirconia Alumina | Stronger than aluminum oxide, handles heat well, sharpens itself, cuts hard | Lasts under high pressure and speed, great for removing lots of material | Gets too hot if pushed too hard, not best for smooth finishes, costs more | Good for making steel parts and grinding stainless steel |
Silicon Carbide | Sharpest grain, breaks easily | Great for clean, sharp cuts and polishing | Not good for hard grinding, breaks easily, not used much in factories | Good for cutting and polishing stainless steel |
Diamond | N/A | N/A | N/A | No data available |
CBN | N/A | N/A | N/A | No data available |
Ceramic alumina and zirconia alumina are the best choices for stainless steel. They last longer and do not get hot as fast as other wheels. Aluminum oxide is good for easy jobs. Silicon carbide is best for polishing. The best grinding wheel for stainless steel depends on what you need to do and how you want it to look.
Aluminum Oxide Grinding Wheel for Stainless Steel
Pros
Aluminum oxide grinding wheels have many good points for stainless steel. These wheels are tough and strong. They can handle high heat and pressure. Many people see that these wheels work well from start to end. This is important for jobs that need careful work. The wheel helps move heat away from the metal. This lowers the chance of burning or hurting the steel.
Aluminum oxide wheels last longer than most other kinds.
They are good for rough and smooth grinding.
These wheels cost less than some other choices.
You can find them in most hardware stores.
If you use them right, they can last even longer.
Cons
Aluminum oxide wheels have some weak points too. They do not last as long as ceramic or zirconia wheels for hard jobs. The wheel can get hot if you use it for a long time. This heat can change the color or shape of the steel. These wheels wear out faster on thick or hard metals. You may need to change them more often for tough work.
Tip: Use light pressure and take breaks to stop overheating.
Best Uses
Aluminum oxide wheels are best for regular grinding jobs. They work well for light and medium tasks on stainless steel. Many shops use them to sharpen tools and smooth welds. They also help clean up edges and finish surfaces. If you want a cheap grinding wheel for stainless steel, aluminum oxide is a good pick.
Zirconia Alumina Grinding Wheel for Stainless Steel
Pros
Zirconia alumina grinding wheels work well on stainless steel. These wheels are very strong and can handle hard jobs. They sharpen themselves while you use them, so they last longer. Many workers pick zirconia alumina when they need to remove metal quickly. The wheel stays in shape even after a lot of use and high pressure.
Very tough under heavy work
Sharpens itself to last longer
Cuts fast for quick jobs
Good for hard metals
These wheels do not wear out fast and can grind big areas. Many shops use them for rough work because they keep working even when the job is hard.
Cons
Zirconia alumina wheels have some downsides. They need you to press harder to work well. If you do not push enough, the wheel can get smooth and stop cutting. This can also make the wheel hotter. Too much heat can change the color or bend the stainless steel. Compared to ceramic alumina, zirconia alumina can get hotter if you do not use enough force. Ceramic alumina wheels stay cooler and need less pressure, so they are better for jobs that need less heat.
Note: Always press steady and firm when using zirconia alumina wheels. This helps stop glazing and too much heat.
Best Uses
Zirconia alumina wheels are best for hard grinding and removing lots of metal fast. They are great when you need speed and strength. Many metalworkers use them to grind welds, shape parts, and take off thick metal. These wheels are good for busy shops that need a strong grinding wheel for tough jobs. If you want a smoother finish or less heat, ceramic alumina is a better pick.
Ceramic Alumina Grinding Wheel for Stainless Steel

Pros
Ceramic alumina grinding wheels stand out for stainless steel work. These wheels use a micro-grain structure that breaks down during grinding. This process exposes new sharp edges and keeps the wheel cutting fast. Workers see longer tool life and better performance on hard metals. Ceramic alumina wheels often last 33% to 100% longer than other ceramic products. Some brands, like Rex-Cut MetalPro, claim up to twice the life of zirconia discs and four times the life of aluminum oxide discs. These wheels need less power to run and hold their shape well at high speeds.
Self-sharpening action keeps the wheel sharp.
Superior heat resistance protects stainless steel from damage.
Longer tool life means fewer wheel changes.
High-speed cutting saves time on big jobs.
Ceramic alumina wheels help workers finish jobs faster and with less effort. The wheel stays cool, so stainless steel does not change color or warp.
Cons
Ceramic alumina wheels cost more than other types. The higher price comes from their premium design and advanced abrasive material. Zirconia alumina wheels cost less and suit mild steel jobs. Aluminum oxide wheels are the cheapest, but they do not last as long. Some users may not want to pay more up front, even though ceramic alumina wheels last longer.
Higher initial cost compared to aluminum oxide and zirconia alumina.
May not be needed for light or small jobs.
Some wheels can break if pushed too hard.
Tip: Choose ceramic alumina wheels for tough stainless steel jobs. The longer life and better finish often save money over time.
Best Uses
Ceramic alumina grinding wheels work best for heavy grinding and finishing on stainless steel. They suit jobs that need a smooth surface and fast metal removal. Many shops use them for weld blending, edge shaping, and surface finishing. Workers pick ceramic alumina wheels when they want the best results and longest tool life.
Ideal for grinding hard stainless steel parts.
Perfect for weld removal and blending.
Great for finishing surfaces without overheating.
Useful in busy shops that need reliable wheels.
Ceramic alumina wheels help workers get a clean finish and save time. The wheel’s long life makes it a smart choice for professionals who work with stainless steel every day.
Silicon Carbide Grinding Wheel for Stainless Steel
Pros
Silicon carbide grinding wheels have special benefits for stainless steel. These wheels use a sharp grain that cuts fast. Workers pick silicon carbide for jobs needing a shiny finish. The grain breaks down as you use it. New sharp edges keep showing up. This helps the wheel cut clean and keeps the finish even.
Makes surfaces brighter than aluminum oxide wheels.
Takes off rust and corrosion but does not hurt the steel.
Good for both light and heavy deburring.
Keeps surfaces flat and smooth while grinding.
Shows new cutting grains for steady work.
Tip: Silicon carbide wheels help get exact finishes on 316 stainless steel. They can keep surfaces flat within 0.001 inch and reach a finish of 32 microinch or better.
Cons
Silicon carbide wheels have some problems too. The grain is sharp but not very tough. This makes the wheel wear out faster, especially on hard metals. Workers may need to change the wheel more often for big jobs. Silicon carbide wheels can break down quickly if you push too hard. They are not good for taking off lots of metal from thick stainless steel.
Wears out faster than ceramic or zirconia wheels.
Not good for heavy metal removal.
Can break or chip if pushed too much.
Costs can go up if you change wheels a lot.
Best Uses
Silicon carbide wheels are great for certain stainless steel jobs. Workers use them for edge breaking, radiusing, and blending. These wheels make a shiny, bright finish that looks nice. They also work well for deburring, both light and heavy, because the resin and grain help remove metal fast. For grinding 316 stainless steel, silicon carbide wheels like Norton black silicon carbide 46 grit are best. They help keep tight size control and a special surface look.
Application Area | Why Choose Silicon Carbide Wheels |
|---|---|
Edge breaking or radiusing | Makes a shiny, bright finish |
Deburring (light and heavy) | Removes metal quickly and easily |
Blending and finishing | Gives a steady, bright finish |
Light corrosion, rust, oxidation removal | Cleans surfaces without hurting the steel |
Surface grinding of 316 stainless steel | Gets exact finishes and tight sizes |
Silicon carbide wheels are good for jobs needing a fine finish and careful work. They help workers clean, blend, and polish stainless steel with confidence.
Diamond and CBN Wheels for Stainless Steel
Pros
Diamond and CBN wheels offer special benefits for grinding stainless steel. CBN wheels, also called cubic boron nitride wheels, stand out for their ability to keep sharp cutting edges. They help workers achieve very smooth and precise finishes on stainless steel. CBN wheels last longer than most conventional wheels. They do not wear down quickly, so workers spend less time changing wheels. CBN wheels also handle heat well. They keep their shape and cutting power, even when grinding creates a lot of heat.
CBN wheels give a smoother and more consistent finish than aluminum oxide or silicon carbide wheels.
They maintain tight tolerances, which means parts come out the right size every time.
CBN wheels show excellent thermal stability, so they do not break down from heat.
Workers can use CBN wheels for longer periods without losing performance.
Diamond wheels are extremely hard. They cut fast and can make very fine finishes on some materials.
Cons
Diamond wheels do not work well on stainless steel. The heat from grinding causes diamond wheels to break down. This makes them less useful for ferrous metals like stainless steel. CBN wheels cost more than regular grinding wheels. Some shops may not want to pay the higher price, even though CBN wheels last longer. Diamond wheels also cost a lot and wear out quickly when used on steel.
Diamond wheels degrade quickly when grinding stainless steel.
Both diamond and CBN wheels have higher upfront costs.
Not every shop needs the high precision these wheels provide.
Note: CBN wheels outperform diamond wheels for stainless steel because they resist heat and keep cutting longer.
Best Uses
CBN wheels work best for jobs that need a perfect finish and tight size control. Workers use them for precision grinding, tool sharpening, and making parts that must fit exactly. CBN wheels help create smooth surfaces with roughness depths less than 1 micron, which is better than most regular wheels. Diamond wheels suit non-ferrous metals and hard materials like ceramics or carbide, but not stainless steel.
Wheel Type | Best Use on Stainless Steel | Not Recommended For |
|---|---|---|
CBN | Precision grinding, tool sharpening, fine finishing | Heavy stock removal, low-budget jobs |
Diamond | Not recommended for stainless steel | Ferrous metals (like stainless steel) |
CBN wheels help workers who need the best finish and longest wheel life. Diamond wheels should be saved for other materials.
Other Factors for Choosing a Stainless Steel Grinding Wheel
Wheel Hardness and Grit
Wheel hardness and grit size play a big role in grinding stainless steel. A wheel with moderate low hardness, such as level J, works best. This type of wheel self-sharpens during use, which keeps the grinding process smooth and efficient. If the wheel is too hard, it can cause heat damage and make the surface rough. If the wheel is too soft, the grains may fall off too soon, making the wheel wear out quickly.
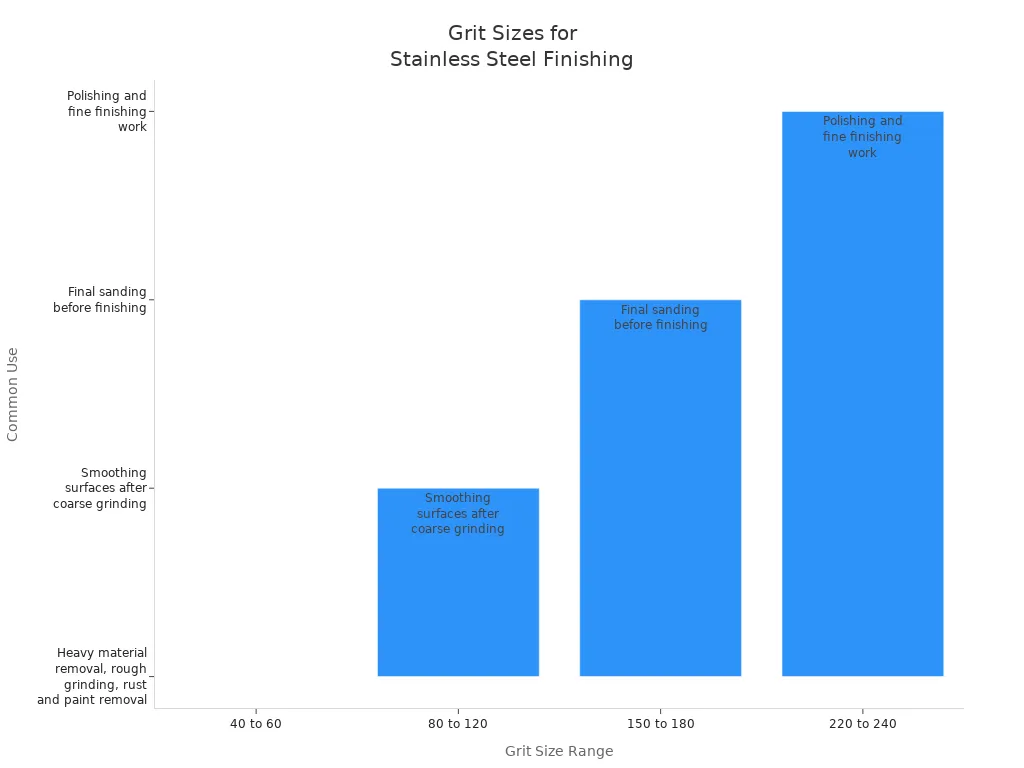
Grit size also matters. Coarse grits, like 40 to 60, remove material fast and help with rough grinding or taking off rust. Finer grits, such as 80 to 240, are better for smoothing and polishing. Workers often start with a coarse grit and move to finer grits for a smooth, shiny finish. Using the right grinding fluid helps prevent burns and scratches on the steel.
Grit Size Range | Common Use for Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
40 to 60 | Heavy material removal, rough grinding, rust removal |
80 to 120 | Smoothing surfaces after coarse grinding |
150 to 180 | Final sanding before finishing |
220 to 240 | Polishing and fine finishing work |
Wheel Shape and Bond Type
The shape and bond of a grinding wheel affect how it works on stainless steel. Type 27 wheels have a flat shape and work best at a 0 to 15-degree angle. They help blend and finish flat or slightly curved surfaces. Type 29 wheels have a conical shape and work at a steeper angle, making them better for removing lots of material quickly.
Wheel Type | Shape Description | Optimal Grinding Angle | Best Use on Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
Type 27 | Flat flap disc | 0 to 15 degrees | Smooth finishing, blending, precision refinements |
Type 29 | Conical flap disc | 15 to 35 degrees | Aggressive stock removal, initial grinding |
Grinding wheels use different bonds to hold the abrasive grains. Resin bonds are flexible and give a smooth finish, but they can get hot and wear out faster. Vitrified bonds are rigid and resist heat, making them good for precision work. Metal bonds last the longest but are less common for stainless steel.
Tip: For stainless steel, resin and vitrified bonds are most popular. Resin bonds suit general grinding, while vitrified bonds help with high-precision jobs.
Heat resistance, waterproofing, and wheel structure also matter. Wheels that resist heat and water last longer and protect the steel from damage. Choosing the right combination of hardness, grit, shape, and bond helps workers get the best results on stainless steel.
How to Choose the Best Abrasives for Stainless Steel
Application and Budget
Picking the best abrasives for stainless steel depends on your job and how much money you have. You need to match the abrasive to what you are doing. Some jobs need heavy grinding, while others need smooth finishing or polishing. Each abrasive has its own good points. Aluminum oxide is good for most jobs and does not cost much. Zirconia alumina is better for hard work and lasts longer. Ceramic abrasives are the toughest and do not get hot, so they are great for hard jobs.
When picking abrasives for stainless steel, workers should think about a few things:
Hardness: Abrasives with high Mohs ratings scratch stainless steel well and last longer.
Surface profile: The size, shape, and amount of abrasive should fit the job.
Surface removal rate: Fast removal saves time but can cost more if the abrasive wears out fast.
Recycling capability: Abrasives you can use again save money in big shops.
Working speed: Faster wheels help finish jobs quickly but may need to be replaced more often.
Bulk density: Abrasives with more density clean faster and make a nicer finish.
Workers should not use the same discs or belts for other metals. This stops steel dust and iron from hurting stainless steel’s rust protection. Picking the right abrasive helps stop dulling, loading, and burning. These problems can waste time and materials.
Tip: Supersize layers on coated abrasives help keep things cool and slippery. This lets you grind more metal before changing the abrasive, which saves money and time.
The abrasive you pick changes how much the job costs. The right wheel, grit, grade, and bond help balance how much metal you remove, how smooth it looks, and how long the tool lasts. Ceramic flap discs last longer and stay cooler, so they are a smart choice for busy shops.
Finish Quality and Tool Life
You often have to choose between a smoother finish or tools that last longer. Finer grains make smoother surfaces but wear out faster. Coarser grains take off more metal and make tools last longer.
The table below shows how different grinding wheel features change finish and tool life:
Parameter | Effect on Finish Quality | Effect on Tool Life / Material Removal Rate |
|---|---|---|
Grain Size | Finer grains create smoother surfaces | Coarser grains last longer and remove more material |
Wheel Grade | Softer wheels give finer finishes | Harder wheels last longer and grind faster |
Abrasive Type | cBN gives precise finishes | cBN resists wear and lasts longer |
Bond Type | Vitrified bonds improve finish and coolant resistance | Metal bonds save cost but may vary in durability |
Ceramic grinding wheels, like ceramic flap discs, are the best for stainless steel when you want a shiny finish. These wheels stay sharp, cut fast, and do not get hot. To get a mirror shine, start with rough abrasives and move to finer ones. Use polishing and buffing wheels and the right compounds to finish the job.
Note: Move the wheel evenly and check your work often. This helps you get an even shine and stops overheating or dirt from ruining the finish.
New grinding wheels, like the 3M™ Cubitron™ 3 Depressed Center Grinding Wheel, use special grains that break into new sharp points. This makes them cut faster, stay cooler, and last longer. Smart sensors and new materials also make grinding safer and more efficient.
To pick the best abrasives for stainless steel, you need to balance how smooth you want it, how long the tool lasts, and how much it costs. Pick abrasives that fit your job, the work area, and the finish you want. Start with rough abrasives and move to fine ones for the best results, whether you need heavy grinding or a shiny finish.
Most people think ceramic alumina and zirconia alumina wheels are best for stainless steel. The table below shows which wheel is good for each job:
Grinding Wheel Type | Recommended Use for Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
Type 1 (Straight) | General grinding and sharpening |
Type 27 (Depressed Center) | Heavy stock removal, weld leveling |
Type 29 (Flexible) | Blending, finishing, curved surfaces |
If you want a smooth finish, use ceramic flap discs or fine grit sanding belts. Always look at heat resistance and how hard the wheel is before picking one. Experts say you should ask suppliers for help with special jobs. Workers need to wear safety gear and keep tools clean. This keeps the steel safe and protects workers too.
FAQ
What grinding wheel works best for stainless steel welds?
Ceramic alumina wheels take off welds fast. They make the surface smooth. Flap discs are used a lot for stainless steel. These discs stay cool and last longer when blending welds.
How does grit size affect stainless steel grinding?
Coarse grit takes off metal quickly but leaves marks. Fine grit makes the surface smooth. Workers pick grit size for the finish they want. Sanding belts help get rough or shiny results on stainless steel.
Can polishing compounds improve stainless steel finishes?
Polishing compounds give stainless steel a shiny look. They remove small scratches and make surfaces bright. Workers use these compounds after grinding and sanding for the best shine.
Are Type 27 and Type 29 wheels different for stainless steel?
Type 27 wheels are good for flat surfaces and blending. Type 29 wheels take off more metal and work on curved surfaces. Workers choose the wheel shape for the job they need to do.
How can overheating be prevented when grinding stainless steel?
Workers use light pressure and stop to cool down. Wheels with good heat resistance help prevent overheating. Coolants or grinding fluids keep the metal safe from heat.
See Also
Choosing The Best Grinding Wheel For Stainless Steel
Finding The Ideal Grinding Wheel Dresser For Your Needs
Selecting The Perfect Metal Grinding Wheel For Projects
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools

