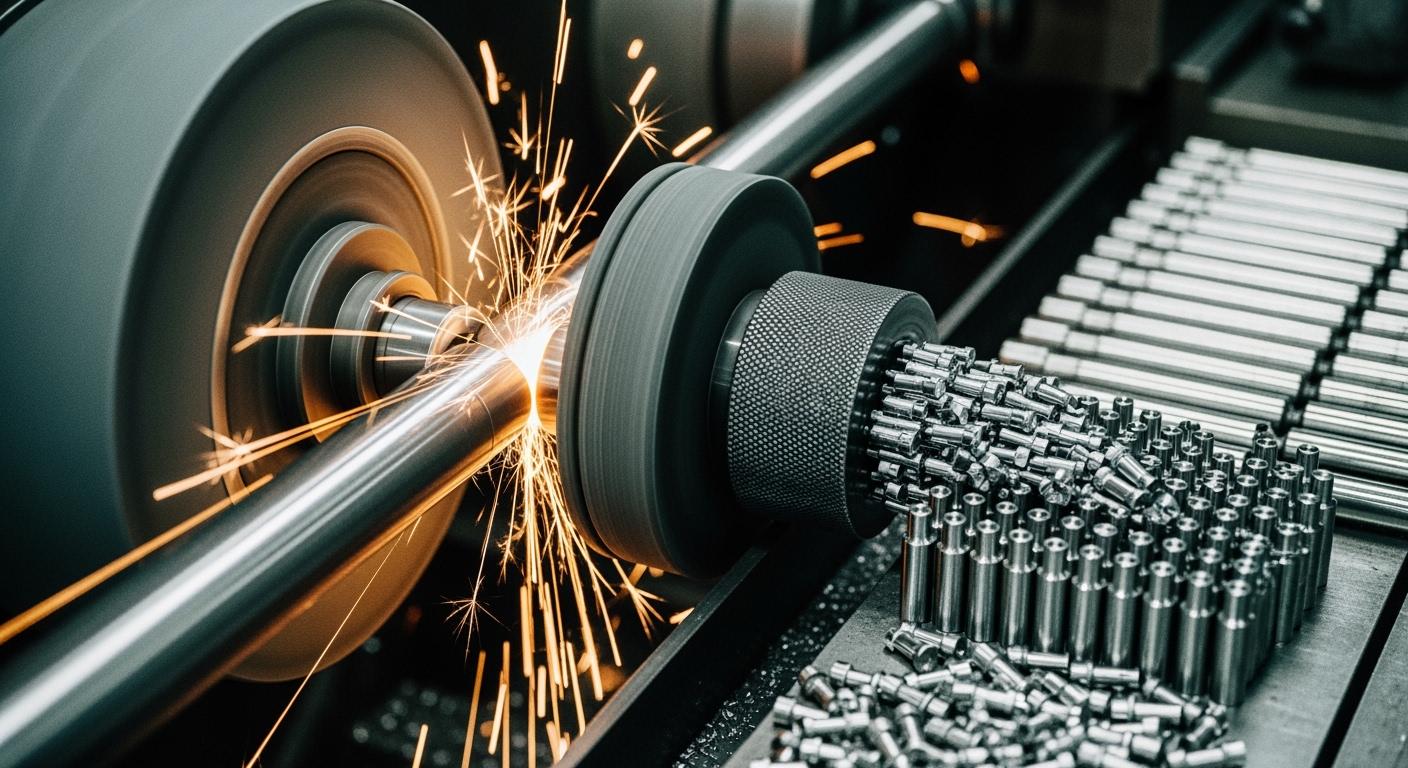
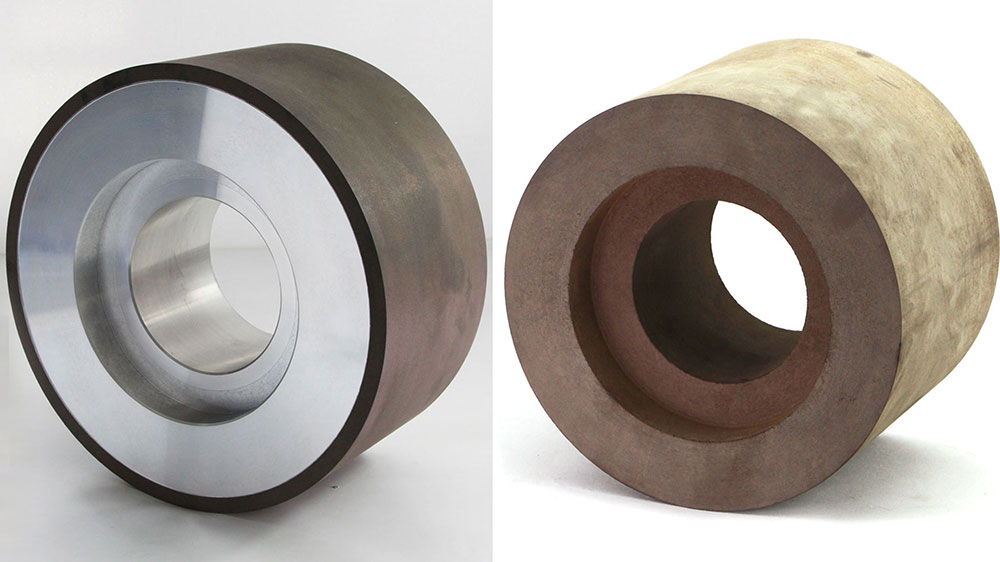
Centerless grinding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. It enables high-volume production by eliminating the time-consuming step of individually centering each workpiece. This continuous, rapid processing relies on two key methods: through-feed and in-feed grinding. The growing significance of centerless grinding is reflected in market projections:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.65 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2031) | 1.24% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
Key Takeaways
- Centerless grinding makes many parts quickly. It does not need to center each part by hand. This saves time and makes production faster.
- This grinding uses three parts: a grinding wheel, a regulating wheel, and a work rest blade. These parts hold the workpiece steady. This helps make round parts with a smooth finish.
- There are two main ways to do centerless grinding. Through-feed grinding is for simple, long parts. In-feed grinding is for parts with complex shapes like shoulders or grooves.
- Centerless grinding saves money and makes parts very fast. It also makes parts very precise. This is important for industries like cars, airplanes, and medical devices.
- Using special grinding wheels, like CBN wheels, helps make a very smooth finish. These wheels work well on tough metals like stainless steel. They keep the parts from getting too hot.
The Principle of Centerless Grinding
The efficiency of centerless grinding stems from its unique operational principles. It fundamentally changes how cylindrical parts are processed. This method relies on a clever system that supports and rotates the workpiece without centers or chucks, enabling continuous, high-speed production.
Eliminating the Centering Process
Traditional grinding requires each part to be individually mounted between centers. This setup process is time-consuming and creates a bottleneck in high-volume environments. Centerless grinding completely removes this step. Parts are fed directly into the grinding machines, dramatically reducing cycle times and simplifying automation. This streamlined workflow is a primary reason for its adoption in mass production, as it accelerates turnaround and boosts overall throughput.
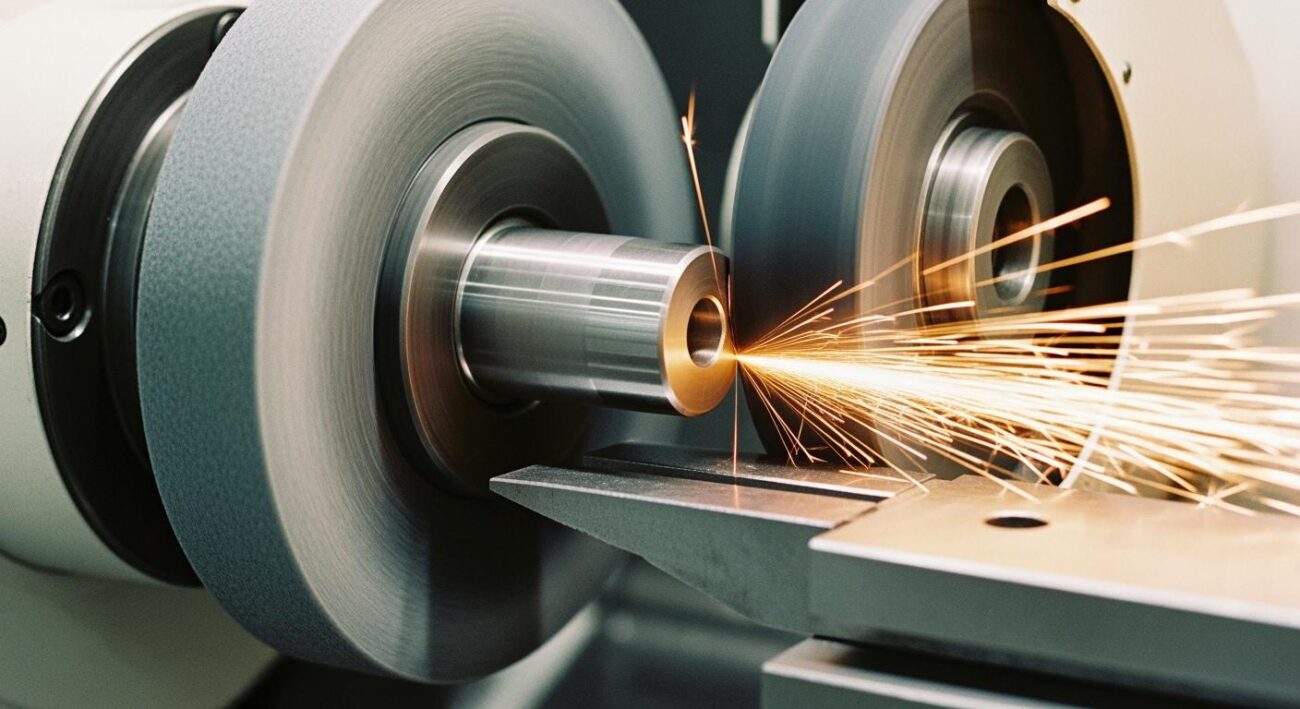
The Three-Point Contact System
The core of centerless grinding is its ingenious three-point contact system. This configuration secures the workpiece using balanced forces instead of mechanical fixtures.
The system consists of three essential components:
- A large grinding wheel that performs the abrasive action.
- A smaller regulating wheel that controls the workpiece’s rotation speed.
- A work rest blade that supports the workpiece from below.
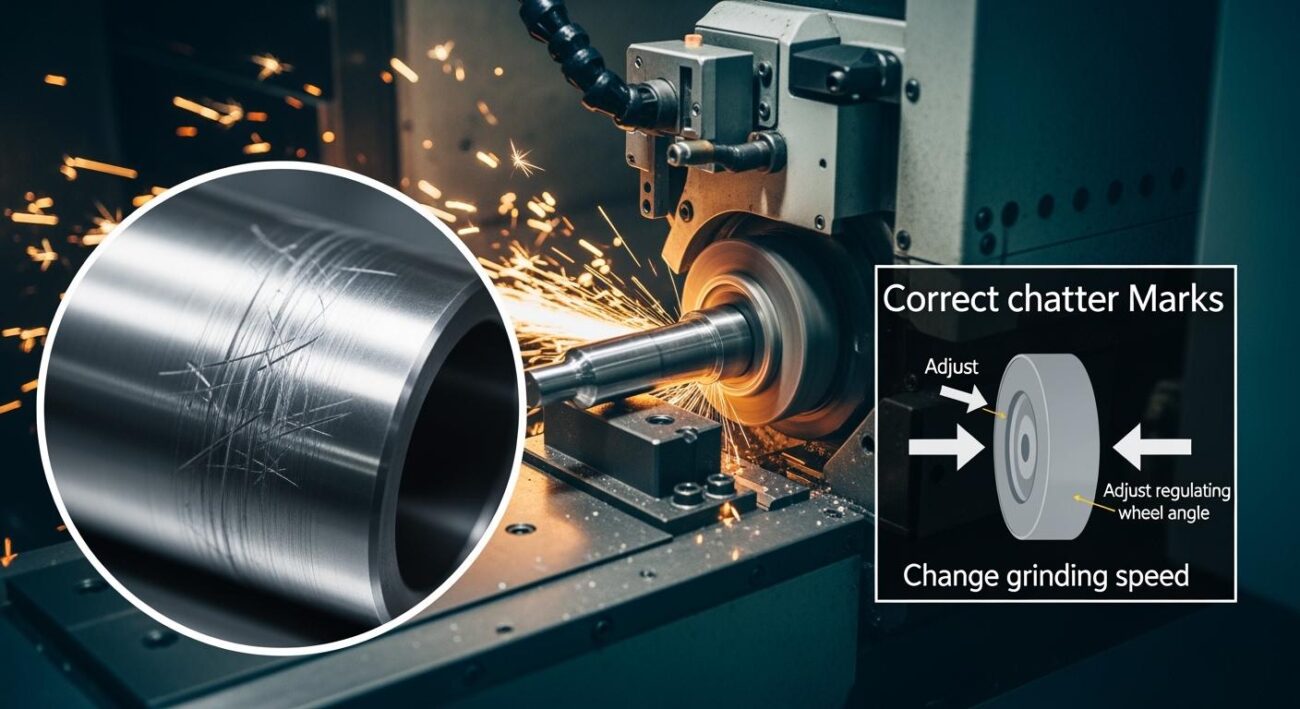
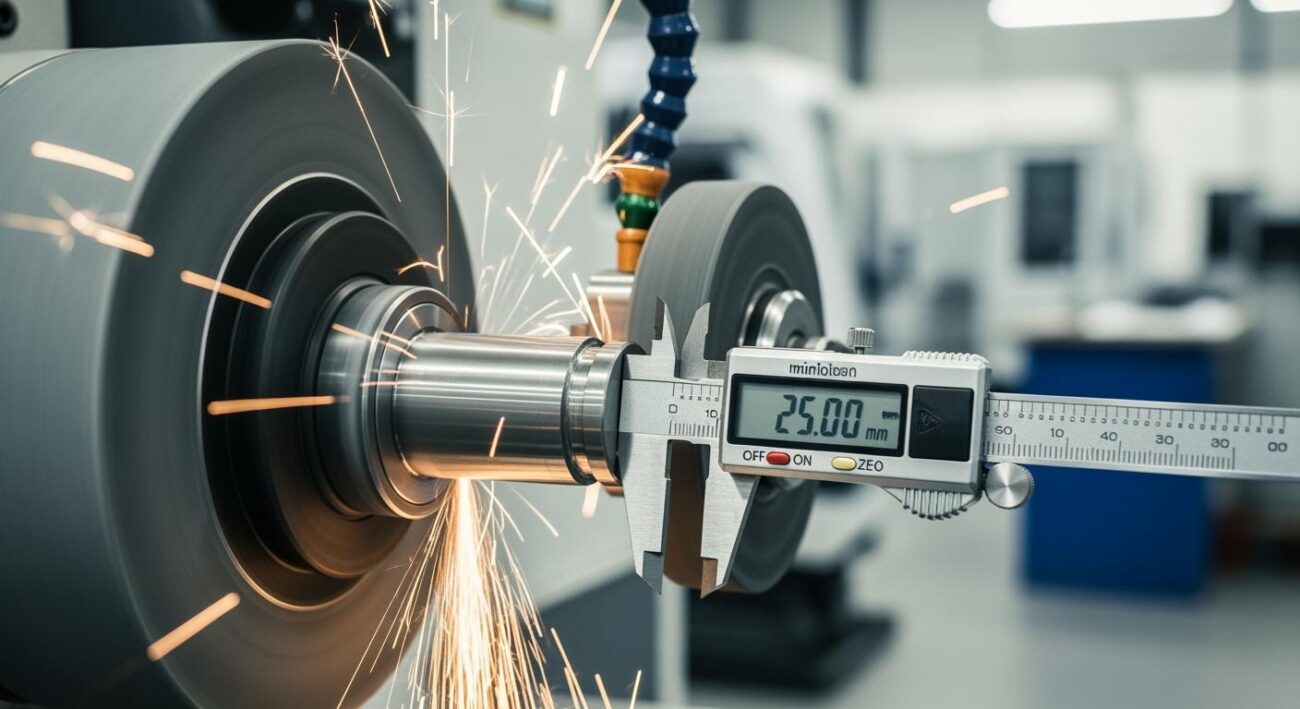
The workpiece rests on the blade, positioned slightly above the centerline of the two wheels. This specific height is critical for achieving roundness and a quality finish. The regulating wheel, often made of a high-friction material, grips the part and spins it at a controlled speed. This rotation ensures the entire surface is ground evenly. The difference in rotational speed between the two wheels dictates the material removal rate. This dynamic interaction allows modern grinding machines to produce parts with an extremely controlled diameter and smooth surfaces. The system naturally dampens vibrations, which contributes to an excellent surface finish and helps maintain tight tolerances. This precise control is essential for achieving a consistent final finish with controlled tolerances across thousands of components.
High-Volume Grinding Methods
Centerless grinding achieves its remarkable productivity through two primary methods. Each method is tailored to specific part geometries and production demands. The choice between them depends entirely on the component’s design and the desired output volume. These techniques are what make modern grinding machines so versatile.
Through-Feed for Continuous Production
Through-feed grinding is the engine of mass production for simple cylindrical parts like pins, rods, and rollers. This method offers unmatched efficiency for components with a uniform diameter. Workpieces are fed into the machine one after another, creating a continuous flow.
The regulating wheel is the key to this process. It is tilted at a slight angle, often denoted as alpha. This inclination generates a consistent axial force, pushing the workpiece through the grinding zone at a controlled feed rate. This action ensures high efficiency and throughput for large batches of identical parts.
The process is automated and requires minimal operator intervention once set up. This makes it the ideal choice for achieving the lowest possible cost per part in high-volume scenarios.
In-Feed for Complex Geometries
In-feed centerless grinding, also known as plunge grinding, is designed for parts with more intricate shapes. This method is essential when a component’s geometry prevents it from passing straight through the machine. The workpiece remains stationary axially while the grinding wheel “plunges” into it to create the desired profile.
This technique is perfect for producing parts that feature:
- Shoulders, grooves, or tapers
- Multiple diameters on a single shaft
- Complex profiles, such as those on valve spools or pump shafts
- Components with a head or projection, like bolts
The grinding wheel is dressed to the negative shape of the final part profile. As the wheel is fed radially into the workpiece, it precisely transfers this complex shape onto the component. This makes in-feed grinding indispensable for manufacturing specialized parts where precision is paramount.
Key Benefits of High-Volume Grinding
Centerless grinding offers significant advantages for high-volume manufacturing. Its unique design delivers speed, cost savings, and precision. These benefits make it an indispensable process in modern production environments.
Unmatched Production Rates
The primary advantage of centerless grinding is its incredible speed. The method eliminates the need to individually mount each part. This allows for a continuous flow of workpieces, dramatically increasing throughput. Through-feed grinding, in particular, can process thousands of parts per hour. This rate is simply unattainable with traditional methods that require manual setup for each component.
A comparison highlights the difference in output:
| Grinding Method | Typical Production Rate (parts per hour) |
|---|---|
| Through-feed Centerless | 1,000 – 5,000 |
| Traditional Cylindrical | 50 – 200 |
Case studies confirm these gains. For example, by implementing technology to reduce chatter, one operation increased its productivity by 100%. The grinding cycle time was cut from 28.3 seconds to just 12.5 seconds per part. This demonstrates the massive potential for boosting efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
High production rates directly translate to lower costs per part. Centerless grinding minimizes cycle times by removing clamping and centering operations. This reduction in non-productive time is a key driver of its cost-effectiveness. Automation further enhances these savings. Automated loading and unloading systems allow grinding machines to run with minimal operator supervision.
This synergy of speed and automation delivers compelling financial returns.
| Metric | Detail |
|---|---|
| Throughput Gains | Automated systems process workpieces 20-30% faster than manual operations. |
| Operating Cost Reduction | Automation typically delivers a 22% reduction in operating costs. |
| Labor Replacement | A single automated cell can replace 2-3 operator positions across multiple shifts. |
Investing in modern equipment with automation capabilities leads to significant improvements across the board. The return on investment comes from higher productivity, better quality, and lower maintenance needs.
Reduced scrap rates and lower energy consumption per part also contribute to the overall savings, making centerless grinding a smart investment for any large-scale manufacturing operation.
Precision with Advanced Abrasives
High volume does not mean sacrificing quality. Achieving a fine surface finish and tight tolerances across thousands of parts requires advanced abrasive technology. The grinding wheel is critical for delivering consistent quality. While conventional wheels wear down quickly, superabrasive wheels maintain their shape and cutting ability for far longer.
This is especially important when working with difficult materials like hardened steels, superalloys, or stainless steel. For these applications, high-performance abrasives are essential. For instance, Aimgrind‘s CBN grinding wheels are engineered for this exact purpose. CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) is one of the hardest materials available, second only to diamond. This hardness allows it to grind tough metals like stainless steel without rapid wear.
The benefits of using advanced abrasives are clear:
| Abrasive Wheel Type | Surface Finish (Ra) | Dimensional Tolerance (microns) |
|---|---|---|
| CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) | 0.05 – 0.2 | ±1 – ±3 |
| Conventional Abrasives | 0.4 – 1.6 | ±5 – ±10 |
CBN wheels offer superior thermal conductivity. They pull heat away from the workpiece, preventing thermal damage and preserving the material’s integrity. This results in a superior surface finish and protects parts from defects. The durability of these wheels ensures a consistent finish from the first part to the last, a key requirement for high-volume production of stainless steel components. Using the right abrasive ensures every part meets specification, providing the consistent quality that modern industries demand. The final finish on a stainless steel shaft, for example, will be smooth and precise every time.
Top Applications for Centerless Grinding
The speed and precision of centerless grinding make it indispensable across several demanding industries. Its ability to produce uniform cylindrical parts at high volume is critical for modern manufacturing. Key sectors rely on this process to meet strict performance and quality standards.
Automotive Components
The automotive industry was an early adopter of this technology. It requires the mass production of interchangeable parts with extreme consistency. Centerless grinding delivers on this need, enabling the high-volume output required for global supply chains. Many critical engine and transmission parts are made this way.
Common automotive components include:
This process helps manufacturers meet stringent automotive quality standards like IATF 16949. It consistently achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.003mm and a surface finish of Ra 0.1μm, ensuring optimal performance for millions of stainless parts.
Aerospace and Defense Parts
Reliability is non-negotiable in the aerospace and defense sectors. Components must withstand extreme conditions without failure. This method is used to produce high-strength cylindrical parts, including many made from tough stainless alloys. The process ensures every part meets exact specifications for fit and function. Key applications include hydraulic and actuator systems, where smooth operation is vital. These precision components often involve durable stainless materials.
Typical parts include:
- Hydraulic pistons and cylinder rods
- Actuator components and bushings
- Turbine blades and gears
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical field demands the highest level of precision and cleanliness. The manufacturing of surgical tools and implants requires flawless surfaces to ensure patient safety and biocompatibility. This is where the stainless steel manufacturing process excels. It is used to create a variety of devices from materials like titanium and medical-grade stainless steel. A smooth finish on a stainless instrument prevents bacterial growth and ensures it can be properly sterilized. The process is ideal for creating a precision-ground shaft for motors in surgical tools or crafting precision-ground stainless bars for implants.
Medical devices must meet strict FDA and ISO 13485 regulations. A fine surface finish is not optional; it is a requirement for function and safety. For example, a stainless cardiovascular stent needs an exceptionally smooth surface to prevent blood clots. The use of high-quality stainless bar stock and precision bars is standard.
This chart shows the required surface finish for various medical parts, from stainless implants to stainless surgical tools.
Centerless grinding’s core strength is its ability to process parts continuously without individual chucking. This streamlined workflow is the foundation of its high-volume production capability. The combination of speed, cost-effectiveness, and precision makes it the definitive choice for mass-producing shafts and pins. Achieving a superior finish on every stainless part, from a stainless pin to a stainless shaft, requires advanced abrasives.
The consistent quality finish on stainless components is unmatched. This process delivers a perfect finish for any stainless application, including stainless medical devices. The final stainless finish is always flawless.
This efficiency is further enhanced by quality abrasives from brands like Aimgrind. Modern integration with IoT also promises to reduce downtime, securing the method’s role in the future of manufacturing for every stainless part.
FAQ
What materials are suitable for centerless grinding?
Centerless grinding works on many materials. It is ideal for metals like steel, aluminum, and titanium. The process is especially effective for producing high volumes of stainless components, including parts made from medical-grade stainless steel. It handles both simple and complex stainless parts with ease.
How does this process achieve a fine finish on stainless steel?
Achieving a mirror-like finish on a stainless part requires the right abrasive. Advanced wheels, like CBN, prevent heat damage. This ensures a smooth surface without discoloration. The final stainless finish is consistent across thousands of parts, from a stainless pin to a stainless shaft.
Can centerless grinding create parts with different diameters?
Yes, the in-feed grinding method is used for this. It is perfect for parts with multiple diameters, shoulders, or tapers. This technique allows for the precise manufacturing of complex components, including specialized stainless parts used in automotive and aerospace applications.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools