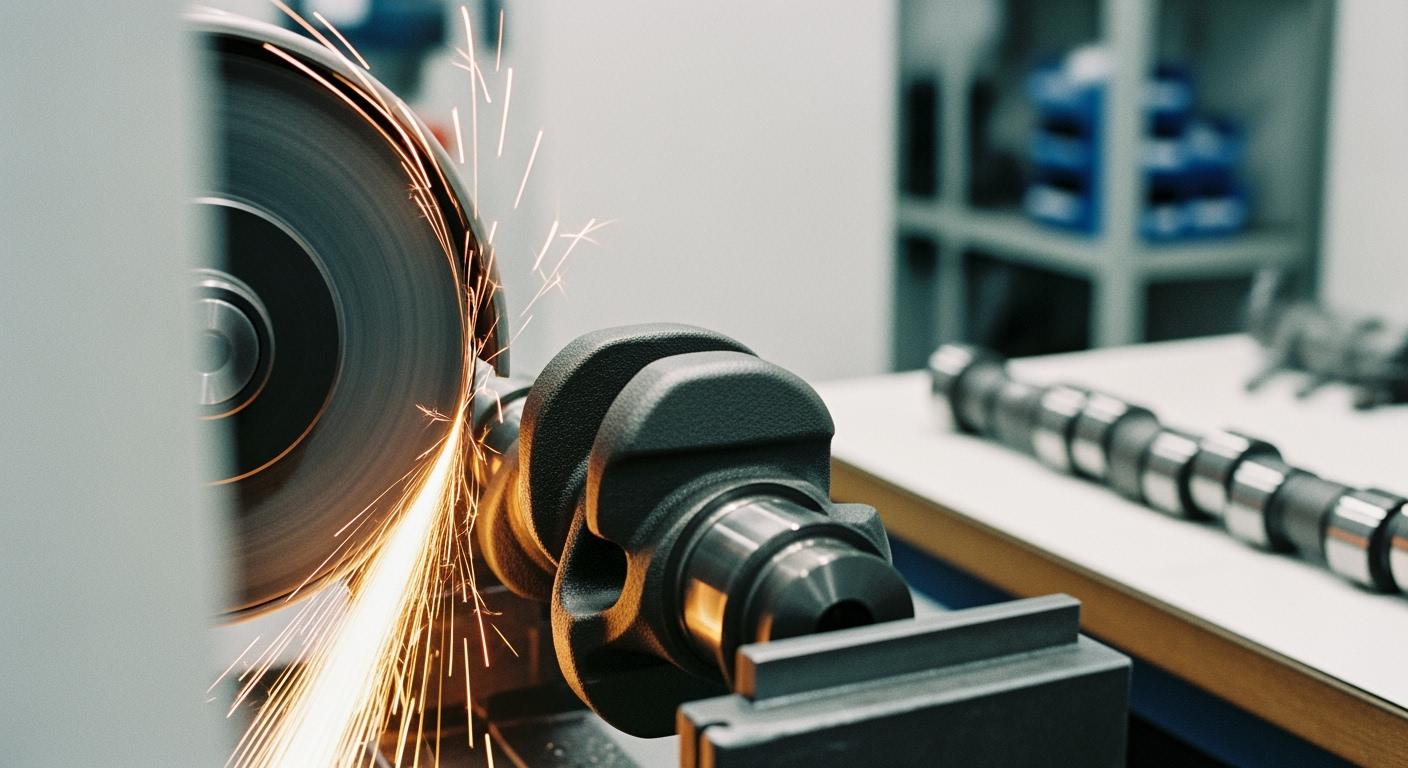
The grinding wheel is a critical tool in camshaft and crankshaft manufacturing. It dictates the final precision, surface finish, and overall productivity. Effective grinding wheel selection provides a clear path to optimal results. For hardened steel components, the industry standard is a superabrasive grinding wheel using Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), which delivers superior performance and part quality.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right grinding wheel for good results in making camshafts and crankshafts.
- Use special CBN wheels for hard metals; they work better and last longer.
- Vitrified bonds are best for exact shapes and keeping the wheel cool.
- Grit size changes how fast you grind and how smooth the part becomes.
- Aimgrind‘s CBN wheels help you grind faster, cooler, and save money.
Abrasive Choice for Your Workpiece

The abrasive material is the heart of the grinding wheel. Its properties must match the workpiece material to ensure efficient and precise results. The choice generally falls into two categories: conventional abrasives for softer metals and superabrasives for hardened steels.
Conventional Abrasives for Softer Metals
Conventional abrasives like Aluminum Oxide and Silicon Carbide are effective for grinding softer, non-hardened metals. Each has distinct characteristics suitable for different tasks. Operators select them based on the specific metal and desired outcome.
| Abrasive Type | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | General-purpose grinding of most steels, aluminum alloys, and bronze. | A tough, durable abrasive that is cost-effective for deburring and stock removal on softer steels. |
| Silicon Carbide | Non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and titanium; also cast iron. | Harder and sharper than aluminum oxide. It provides a cooler cut and a finer finish on softer, ductile metals. |
While useful for initial stages or softer components, these abrasives lack the durability needed for hardened camshafts and crankshafts.
Superabrasives for Hardened Steels
Superabrasives are necessary for grinding hard ferrous metals. Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is the industry standard for this work. It offers unmatched performance on materials that are too hard for conventional abrasives.
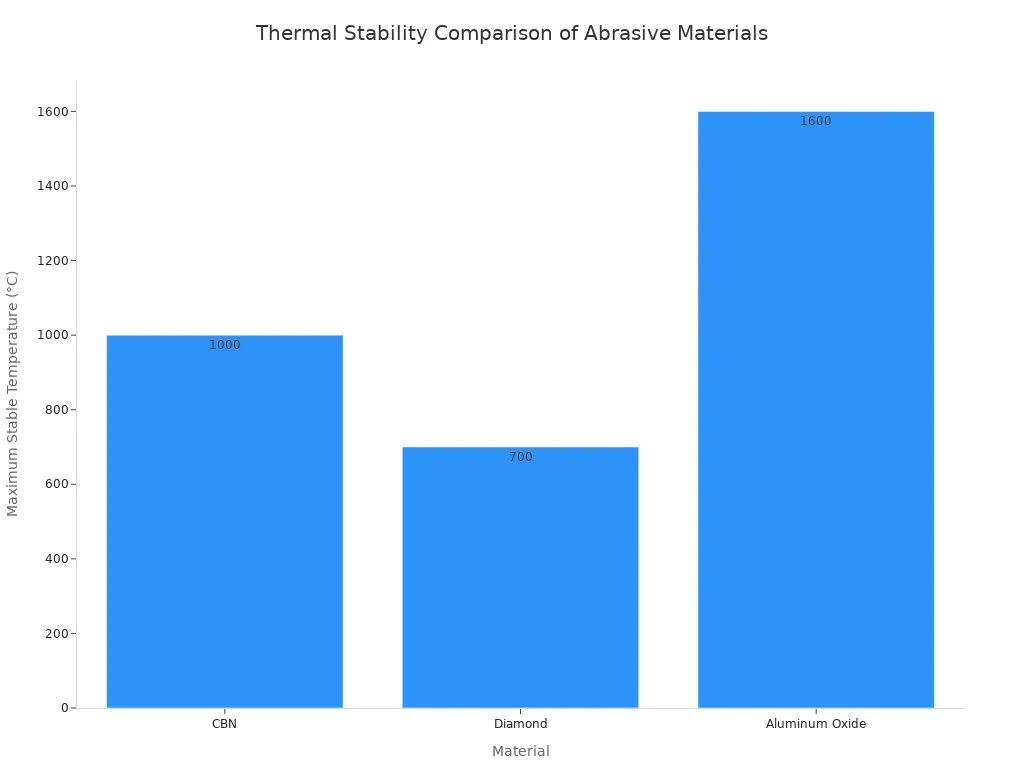
Pro Tip: 💡 CBN becomes the most effective and economical choice for grinding ferrous metals with a hardness above 45 HRC (Rockwell C scale).
The primary advantage of a CBN grinding wheel is its exceptional thermal stability. CBN maintains its hardness at extreme temperatures and does not chemically react with iron. This prevents workpiece damage and allows for faster, cooler grinding operations. In contrast, other abrasives either lose hardness or react with steel at high temperatures.
Choosing the right abrasive formula is vital. Aimgrind specializes in customized grinding solutions. The team can design the perfect abrasive formula for the specific steel alloys or superalloys used in a modern high-performance engine, ensuring your grinding wheel delivers peak efficiency.
The Role of the Bond System
The bond system acts as the glue holding the abrasive grains together in a grinding wheel. It determines the wheel’s strength, flexibility, and overall characteristics. The choice of bond type in grinding performance is critical, as it directly influences how the wheel interacts with the workpiece. For camshaft and crankshaft production, vitrified and resinoid bonds are the most common choices, each serving a distinct purpose.
Vitrified Bonds for Precision and Form Holding
Vitrified bonds are created by fusing glassy or ceramic materials at high temperatures. This process results in a strong, rigid, and porous structure. These bonds excel in precision grinding operations where holding a specific shape is essential. Industries like automotive and aerospace rely on vitrified bond wheels for manufacturing engine components, turbine blades, and cutting tools.
The porous nature of a vitrified grinding wheel offers two key advantages:
- Coolant Delivery: Pores act as channels, allowing coolant to flow directly to the grinding zone. This prevents thermal damage to the workpiece.
- Chip Clearance: The open structure provides space for metal chips to escape, preventing the wheel from loading and maintaining its cutting efficiency.
Application Insight: ⚙️ For grinding hardened steel camshafts and crankshafts, a vitrified CBN grinding wheel is the superior choice. Its rigidity ensures tight tolerances are met, while its porosity allows for cool, efficient material removal.
Resinoid Bonds for Fine Finishes
Resinoid bonds use synthetic resins to hold the abrasive grains together. These bonds are cured at lower temperatures than vitrified bonds. This process gives them a degree of elasticity and shock absorption. The selection of this bond type in grinding performance is ideal for operations requiring a smooth surface finish or tasks involving heavy stock removal.
The slight flexibility of resinoid bonds helps absorb vibrations and impacts. This makes them suitable for applications like cut-off operations and rough grinding, where mechanical stress is high. While not the primary choice for the final precision grinding of camshafts, they can be used in earlier stages or for finishing operations where a very fine surface is the main goal. Their ability to produce excellent finishes makes them valuable in specific, less dimensionally critical applications.
Key Grinding Wheel Specifications
Beyond the abrasive and bond, three core wheel specifications—grit size, grade, and structure—determine a grinding wheel’s performance. Understanding these parameters is essential for fine-tuning the grinding process for camshafts and crankshafts. Correctly defining these wheel specifications ensures optimal results for each specific application.
Grit Size: Removal Rate vs. Surface Finish
Grit size refers to the size of the individual abrasive grains in the wheel. This is a critical choice that balances material removal speed against the final surface quality.
- Coarse Grits (e.g., #24-#60) have larger abrasive particles. They remove material quickly, making them ideal for roughing operations where speed is a priority.
- Fine Grits (e.g., #80-#220+) have smaller particles. They remove less material per pass but produce a much smoother surface finish, which is necessary for meeting tight tolerances.
For hard materials like hardened steel, finer grits are often required to achieve the desired finish without causing thermal damage. The selection of these wheel specifications depends on the grinding stage.
| Grinding Stage | Typical Grit Size Range |
|---|---|
| Rough Grinding | 60 – 80 grit |
| Finish Grinding | 120 – 180+ grit |
Grade: Wheel Hardness and Wear Resistance
The grade of a grinding wheel indicates the strength of the bond holding the abrasive grains. It is often called wheel hardness. This property is measured on an A-Z scale, where ‘A’ is the softest and ‘Z’ is the hardest.
Pro Tip: 💡 A softer grade wheel releases dull abrasive grains more easily, exposing fresh, sharp grains. This is useful for heat-sensitive materials. A harder grade wheel holds onto its grains longer, making it durable for high-pressure, high-volume production runs.
| Hardness Grade | Code |
|---|---|
| Soft | H, J, K |
| Medium | L, M, N |
| Hard | P, Q, R, S |
Choosing the right grade from the available wheel specifications is a balance. A wheel that is too hard can cause burning, while one that is too soft will wear down too quickly.
Structure: Chip Clearance and Coolant Flow
Structure refers to the spacing between the abrasive grains. It is rated on a numerical scale from 1 (most dense) to 16 (most open). A dense structure has less space between grains, while an open structure has more. This feature of the grinding wheel is vital for efficiency.
An open structure provides better chip clearance and allows coolant to flow more freely to the grinding zone. This prevents the wheel from “loading” with metal particles and reduces heat buildup, which is crucial when grinding hardened steel components.
Application-Specific Wheel Selection
Matching a grinding wheel to a specific application moves beyond general specifications. The unique geometries of camshafts and crankshafts demand wheels designed for their distinct challenges. This section explores the optimal wheel choices for both crankshaft grinding and camshaft machining.
Wheel Selection for Crankshaft Grinding
Crankshaft grinding is a highly demanding process. It involves grinding multiple surfaces to precise diameters and finishes. The two primary operations in crankshaft grinding are main journal grinding and crankpin grinding.
- Main Journal Grinding: The main journals are aligned with the crankshaft’s axis. This allows for a standard plunge grinding operation. Manufacturers can use a single-rib wheel for each journal or a multi-rib wheel to grind multiple journals at once, increasing efficiency.
- Crankpin Grinding: This operation is more complex. The crankpins follow an orbital path, so the grinding wheel must move in sync with the workpiece rotation. This requires sophisticated CNC controls to maintain roundness and accuracy during crankshaft grinding.
For both operations, a vitrified CBN grinding wheel is the industry standard. Its rigidity is essential for holding the tight tolerances required in crankshaft grinding. The porous structure ensures coolant reaches the cutting zone, preventing thermal damage on these critical surfaces. The success of crankshaft grinding depends heavily on the wheel’s ability to maintain its form.
Dressing for Precision ⚙️
While a CBN wheel performs the grinding, its profile must be perfectly maintained. Operators use diamond profile wheels to dress the CBN wheel. This critical step reshapes the wheel, ensuring every crankshaft meets exact specifications. This process is fundamental to quality control in crankshaft grinding.
Wheel Selection for Camshaft Machining
Camshaft machining presents a different set of geometric challenges. The primary task is grinding the non-round cam lobes, which control engine valve timing. This process is far from a simple cylindrical grind.
Modern camshaft machining relies on advanced CNC grinders. These machines synchronize the wheel’s infeed and retraction with the workpiece’s rotation to produce the complex lobe shape. CAM software often generates these precise tool paths. The transient nature of camshaft machining means the material removal rate fluctuates, which can cause temperature spikes and localized burns. This makes the choice of wheel critical for successful camshaft machining.
Quality control in camshaft machining is extremely strict. While there are no universal numerical standards for chatter, engine manufacturers have their own tight specifications to ensure low engine noise and prevent vibrations. Achieving these standards requires a wheel that delivers a flawless surface finish. A vitrified CBN wheel provides the cool cutting action and form-holding ability needed for high-performance camshaft machining. Both single-rib and multi-rib wheels are used, depending on the specific camshaft machining operation. The precision of camshaft machining directly impacts engine performance.
Aimgrind’s CBN Grinding Wheels for Peak Performance
For manufacturers pursuing peak efficiency in crankshaft grinding and camshaft machining, the choice of wheel is a strategic decision. Aimgrind’s vitrified CBN grinding wheels are engineered to meet these challenges head-on. They offer a powerful combination of advantages that translate directly to better parts and lower production costs.
The key benefits of Aimgrind’s CBN wheels include:
- Faster Cutting: Increased material removal rates shorten cycle times and boost productivity.
- Cooler Operation: Superior thermal stability minimizes the risk of thermal damage, protecting the workpiece and ensuring a superior surface finish.
- Longer Life: Exceptional wear resistance means the wheel lasts longer, reducing downtime for wheel changes and lowering the total cost per part.
These advantages are not just theoretical. In high-volume production environments, they lead to tangible improvements in workpiece quality and operational efficiency. Aimgrind understands that machine compatibility is crucial. The team specializes in creating customized solutions, ensuring the overall quality of the wheel is perfectly matched to your equipment and process. This tailored approach maximizes the performance of any crankshaft grinding or camshaft machining setup.
Selecting the right grinding wheel is a methodical process. It involves matching the abrasive, bond, and specifications to the material and operational goal. For high-precision, high-volume production of hardened steel parts, Aimgrind’s Vitrified CBN grinding wheels offer a superior combination of speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Partnering with specialists can significantly reduce processing time and costs. Consult with Aimgrind to receive a personalized wheel recommendation that optimizes your specific grinding process.
Grind with Passion, Achieve with Aim.
FAQ
Why is CBN better than diamond for grinding steel?
Diamond chemically reacts with iron at high temperatures, causing rapid wear. CBN is thermally stable and does not react with steel. This makes CBN the superior choice for grinding hardened ferrous metals, ensuring longer wheel life and better part quality.
What is wheel dressing and why is it important?
Wheel dressing is a maintenance process. It uses a tool to restore the grinding wheel’s shape and expose fresh abrasive grains. This step is essential for maintaining precision and consistent performance, especially in high-volume crankshaft and camshaft production.
How does grit size affect the final part?
Grit size determines the balance between speed and finish. Coarse grits remove material quickly but leave a rough surface. Fine grits create a very smooth finish but work more slowly. The correct choice depends on the specific grinding operation.
Can one wheel be used for both roughing and finishing?
Using one wheel for both tasks is not ideal. A coarse wheel is best for roughing to remove stock quickly. A separate, finer grit wheel is then used for finishing. This two-step process ensures both efficiency and high-quality surface results.
How do I choose the right wheel for my specific machine?
The ideal wheel depends on the machine, material, and process. Specialists analyze these factors to recommend a custom solution. Consulting with experts like Aimgrind ensures the wheel is perfectly matched to the equipment for optimal performance and efficiency.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools

