Metal bond grinding wheels are special in the grinding world. They last a long time and do not wear out fast. They are also very precise. These wheels have a metal matrix that holds abrasive grains. This helps the grains stay in place during grinding. It also stops the grains from falling out, even with hard materials. Metal bond grinding wheels move heat better than resin or vitrified bond wheels. But they need special tools to keep them working well. They can also get hotter during use. People pick these wheels when they need steady work and high accuracy.
Key Takeaways
-
Metal bond grinding wheels last a long time. They keep their shape well. This makes them good for grinding hard things like ceramics and glass.
-
These wheels are very precise. They move heat away fast. This helps protect the workpiece. It also gives a smooth finish.
-
Metal bond wheels need special care. They do not sharpen themselves. They are harder to dress and true than other wheels.
-
Advanced dressing methods can help the wheels work better. Hybrid bonds can also make care easier.
-
Metal bond wheels cost more money. But they last longer and are more accurate. This makes them a good choice for hard grinding jobs.
Metal Bond Grinding Wheels: Definition and Types

Basic Definition
Grinding wheels with abrasive grains held by metal bonds (e.g., bronze, nickel, cobalt).
A metal bond grinding wheel holds abrasive grains using metal like bronze, nickel, or cobalt. This makes the wheel strong and stable. The metal bond keeps the grains in place during grinding. It works well even with hard or brittle materials. Many industries use these wheels because they last long and keep their shape. They are used in aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor work. Metal bond grinding wheels do not wear out fast. They can also handle high heat. This makes them good for tough grinding jobs.
High bond strength, suitable for precision grinding.
The strong metal bond helps with precise grinding. Metal bond cbn wheels and cbn bond wheels give good control. These wheels keep their shape well. This is important for jobs that need smooth finishes and tight sizes. The strong bond means the wheels last a long time. They also work well even with heavy use.
Types of Metal Bond Wheels
Sintered Metal Bond (e.g., Bronze Bond): Low-temperature sintering, porous structure.
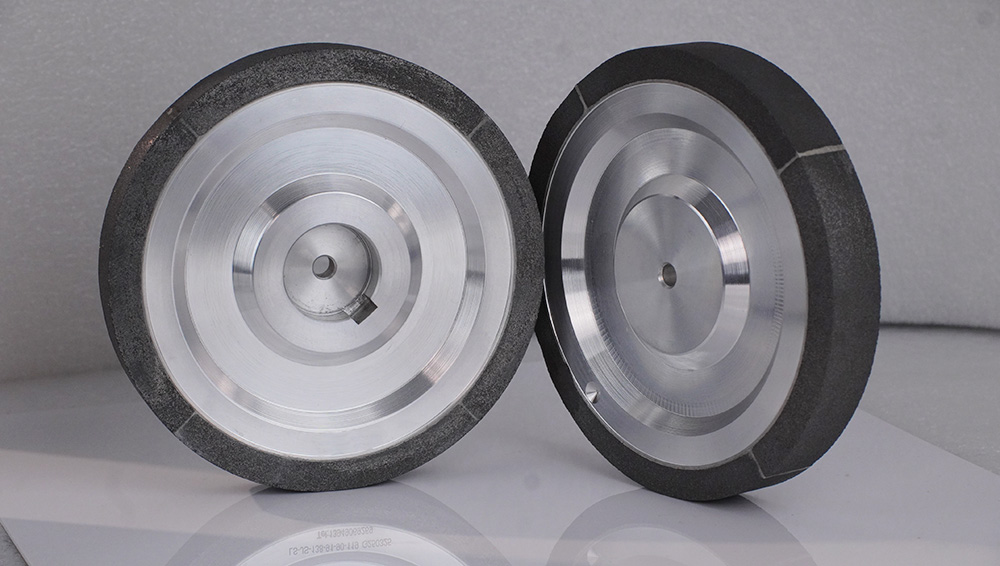

Sintered metal bond grinding wheels are made by pressing metal powder and abrasive grains together. They are then heated at low temperatures. This makes small holes in the wheel. The holes help coolant flow and remove chips during grinding. Sintered wheels are often used for precise work on ceramics and glass.
Electroplated Bond: Single-layer grains bonded via electroplating (Ni/Co).
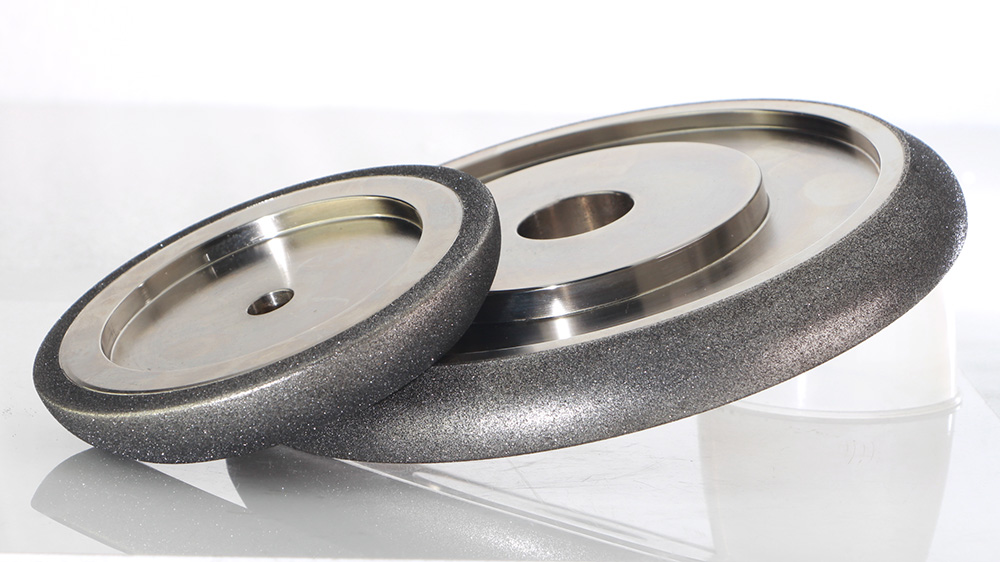

Electroplated metal bond cbn wheels have one layer of abrasive grains. These grains are stuck to the wheel with electroplating, using nickel or cobalt. These wheels cut sharply and are easy to shape for special jobs.
Brazed Bond: Grains bonded via high-temperature brazing (e.g., Ag/Cu alloy).

Brazed metal bond grinding wheels use high heat to attach abrasive grains. They use alloys like silver or copper. This makes a strong bond and lets the wheel grind hard. Brazed wheels are good for heavy-duty grinding.
Clarification: Electroplated and brazed wheels are subsets of metal bond wheels.
Note: Electroplated and brazed wheels are both types of metal bond grinding wheels. Each type is used for different jobs, depending on the material and how exact the work needs to be.
|
Type |
Bonding Method |
Key Features |
Typical Grinding Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sintered |
Low-temp sintering |
Has holes, strong, precise |
Ceramics, glass, hard metals |
|
Electroplated |
Electroplating (Ni/Co) |
Sharp, one layer, easy to shape |
Custom shapes, fast material removal |
|
Brazed |
High-temp brazing |
Strong, grinds hard, lasts long |
Heavy-duty, high removal rate |
Advantages of Metal Bond Grinding Wheels
High Durability and Wear Resistance
Metal bond grinding wheels last longer than other types. They are very tough and do not wear out fast. This makes them a good choice for hard jobs. People use them when they need the wheel to work for a long time.
-
Metal bond wheels are strong and can handle tough materials like glass and ceramics.
-
Resin bond wheels are good for many uses, but metal bond wheels work better for hard jobs.
-
Vitrified bond wheels are precise, but metal bond wheels do better with heavy work.
A table below shows what affects how long the wheel lasts and how well it works:
|
Factor |
Impact on Performance and Wear Resistance |
|---|---|
|
Bond Composition |
Makes the wheel hard and strong, so it lasts longer |
|
Sintering Parameters |
Right heat and pressure help the wheel last longer |
|
Grain Distribution |
Even grains make the wheel stronger and work better |
|
Mechanical Load |
Heavy work needs a strong wheel to last |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Good at moving heat, so the wheel works well when hot |
These wheels can take a lot of heat and heavy work. They keep cutting well, even when the job is hard.
Superior Grinding Precision
Metal bond grinding wheels are very precise. The metal holds the grains tight, so they do not fall out. This keeps the wheel in shape and gives a smooth finish. These wheels use small grains for fine work and smooth surfaces.
These wheels are great for hard things like ceramics and carbides. The metal bond helps the grains cut better and last longer. New ways to make these wheels let people pick special shapes for their jobs.
High Thermal Conductivity
Metal bond grinding wheels move heat away fast. This stops the workpiece from getting too hot or damaged. Tests show these wheels do not burn the workpiece and keep it strong. They give a smooth finish and last a long time. This makes them good for jobs that need a nice surface and long use.
Disadvantages of Metal Bond Grinding Wheels
Low Self-Sharpening Ability
Dull grains remain, increasing grinding force/heat.
Metal bond grinding wheels do not clean themselves well. Vitrified bond diamond grinding wheels let old grains break off. This shows new sharp edges. Metal bonds keep dull grains stuck in place. The wheel can get shiny and smooth over time. This makes it harder to grind. More force is needed, and the workpiece gets hotter. People may see the wheel not working as well. The surface can look rougher. Grinding takes longer and is not as good as with wheels that clean themselves better.
Note: Vitrified bonds let old grains break and fall away. Metal bonds do not do this. This changes how the wheels work and how often they need care.
Difficult Truing and Dressing
Hard bond material complicates wheel conditioning.
Metal bond grinding wheels are hard to fix and shape. The strong bond makes it tough to get the right shape back. People have many problems when fixing these wheels:
-
If truing or dressing is not done right, the finish can be bad. Parts may not fit, and the wheel can break.
-
The wheel must be lined up just right to spin true.
-
If the wheel is not balanced, it can shake and leave marks.
-
The right tools must be used to clean off old grains and extra bond.
-
If cleaning is not done well, the wheel can get clogged and not work right.
-
Keeping the wheel round, balanced, and shaped right is hard but needed for good grinding and safety.
These problems make taking care of metal bond wheels harder than resin bond diamond grinding wheels.
Higher Cost
Expensive raw materials (e.g., diamond/CBN + metal powder).
Metal bond grinding wheels cost more than most other wheels. Many things make them pricey:
-
Metal bonds are one of the most costly types.
-
Bigger wheels use more material and cost more.
-
More abrasive material in the wheel raises the price.
-
Jobs that need tight sizes make the cost go up.
-
The core matters too: steel cores are heavy and cost more to ship than Bakelite.
These reasons make metal bond wheels a big cost, especially for shops that need lots of wheels or change them often.
Mitigation Strategies for Disadvantages
Hybrid Bond Solutions
Add porous additives (e.g., ceramic phases) to improve self-sharpening.
Hybrid bond grinding wheels mix resin and metal bonds. This mix helps fix problems with regular metal bond wheels. The resin makes the wheel easier to use and care for. The metal keeps the wheel strong and long-lasting. These hybrid wheels do not need as much force to grind. They are not as hard as full metal bond wheels. For example, EVO Hybrid Bond wheels help people cut better and work easier. Scientists keep working on new hybrid bonds. They want to make wheels that fit special jobs and work faster.
Porous additives like ceramic phases make these wheels even better. These tiny holes help the wheel clean itself. Shapes like honeycomb or octahedron help chips move away from the grains. This design lets more coolant reach the wheel. It also helps heat leave the grinding area. Open pores work better than closed ones. They let coolant and heat move more easily. Wheels with these features stay sharp and cut well. They work best when grinding is tough.
Advanced Dressing Techniques
Laser dressing or EDM for precise shaping.
Advanced dressing techniques help shape metal bond grinding wheels. Laser dressing uses a strong light beam to remove metal fast. It shapes the wheel without touching it. EDM dressing uses electricity to take off metal with great care. Both ways can make detailed shapes and help the wheel work better. Laser dressing is good for the environment and can change for different jobs. EDM dressing works right on the grinding machine. This means less chance for mistakes. People must watch the settings to stop heat damage or tool wear. These methods help the wheel last longer and work better.
|
Aspect |
Laser Dressing |
EDM Dressing |
|---|---|---|
|
Efficiency |
High, easy automation |
Fast, integrated on machines |
|
Cutting Performance |
Better surface quality, complex shapes |
High precision, intricate profiles |
|
Challenges |
Heat-affected zones, parameter control |
Electrode wear, waste liquid management |
Optimized Grain Concentration
Balance grain density to reduce clogging.
Changing how many grains are in the wheel helps stop clogging. It also helps the wheel cut better. More grains can make grinding harder. But with the right bond, the wheel works well and lasts longer. If the grains are balanced, the wheel does not clog as much. Lowering the depth of cut helps too. It keeps the wheel cool and stops grains from falling out. This makes the wheel last longer and keeps the surface smooth.
Tip: Picking the right amount of grains and bond mix helps the wheel cut well and last long, even for hard jobs.
Dressing Methods for Metal Bond Wheels
Mechanical Dressing
Diamond rollers/tools for coarse shaping.
Mechanical dressing is the most common way to fix metal bond wheels. Workers use diamond rollers or tools to shape the wheel and show new abrasive grains. This keeps the wheel working well, especially when a lot of material needs to be removed. But this method can make grains flat or pull them out. That can make the wheel cut less well and change how chips form. Tools wear out fast, and the process is not very efficient. Still, it is simple and many shops use it because it works.
Some new mechanical dressing methods are being studied:
-
Electrolytic In-Process Dressing (ELID) is good for metal-bonded wheels. It works well when grinding hard things like silicon nitride ceramics.
-
Magnetic-Assisted Polishing (MAP) uses a mix with iron powder and cerium oxide. It polishes and dresses wheels, keeping them sharp and working well.
-
Hybrid processing mixes grinding with MAP. This helps remove a lot of material and makes surfaces very smooth.
-
Things like grit size, how deep the tool presses, and how fast it spins are important for making the process better.
-
Silicone pads in MAP help protect the workpiece and make the surface nicer.
Note: MAP with a #2000 grit wheel at low speed can make the surface very smooth, even below 0.014 μm Ra.
Non-Traditional Methods
Electrical Discharge Dressing (EDD): Effective for conductive bonds.
Laser Dressing: High precision, no mechanical contact.
Non-traditional ways to dress wheels have big benefits. Electrical Discharge Dressing (EDD) and Wire Electrical Discharge Conditioning (WEDC) use electricity, not force. These ways keep the grains sharper, lower grinding force, and make the wheel last longer. WEDC is good for making shapes right and doing the same thing every time. It does not touch the wheel, so tools do not wear out. It also saves time because you do not need to shape the wheel first.
Laser dressing uses a strong light beam to take off material from the wheel. It is very exact and does not touch the wheel, so it is good for tricky shapes. But if not careful, pulsed laser dressing can make the wheel too hot and cause damage. EDD and WEDC use water-based fluids to keep things cool and stop heat problems.
|
Dressing Method |
Key Benefit |
Limitation |
|---|---|---|
|
Mechanical (Diamond) |
Simple, widely used |
Tool wear, lower efficiency |
|
ELID/MAP |
Nano-level finish, sharp |
Complex setup |
|
EDD/WEDC |
High precision, no wear |
Needs conductive bonds |
|
Laser Dressing |
No contact, complex shapes |
Risk of thermal damage |
Operators should pick the dressing method based on the wheel type, how exact the job needs to be, and what kind of grinding is being done.
Additional Considerations
Application Suitability
Best for hard/brittle materials (e.g., tungsten carbide, optical glass).
Metal bond grinding wheels are used in many tough jobs. They are strong and last a long time. The metal matrix holds the abrasive grains tightly. This makes the wheel keep its shape even with hard work. These wheels work well on hard or brittle things like tungsten carbide and optical glass. They give a smooth finish and do not wear out fast.
Many industries use metal bond wheels for hard jobs. Some common uses are:
-
Shaping and polishing stone like granite or marble
-
Sharpening tools to keep them cutting well
Metal bond wheels are better than resin bond wheels for tough jobs. They remove more material and can handle high pressure. These wheels last longer and keep their shape. This helps make the finish even. The hard bond stops the grains from coming loose. This is good for strong machines and small surfaces. Metal bond wheels are best when you need steady results and long life.
Tip: If you need a smooth finish on hard things, metal bond wheels usually work better than other types.
Environmental Impact
Metal bonds are recyclable but energy-intensive to produce.
Metal bond grinding wheel makers are trying to be more green. They want to make less waste and recycle more during production. This helps the environment. Metal bonds can be recycled, which is good for the planet. But making these wheels still uses a lot of energy, especially with metals like nickel or cobalt. The industry is working to be better for the earth. When picking a wheel, think about both recycling and how much energy it takes to make.
|
Environmental Factor |
Impact on Metal Bond Wheels |
|---|---|
|
Recyclability |
High—metal bonds can be recycled |
|
Energy Use |
High—production is energy-intensive |
|
Waste Reduction Efforts |
Increasing in modern manufacturing |
Metal bond wheels last a long time and are very strong. They keep their shape well. This makes them great for hard and brittle materials. But they cost more and work slower than some other wheels. People should think about these good and bad points before picking a wheel. It is important to look at how hard the material is. You should also think about how many parts you need to make. Some jobs are simple, but others are more complex. The table below shows how different bond types work for different needs:
|
Bond Type |
Best Use Case |
Wheel Life |
|---|---|---|
|
Metal Bond |
Hard, abrasive materials |
Longest |
|
Vitrified Bond |
High-speed, precision jobs |
Moderate |
|
Electroplated |
Complex shapes, fast removal |
Shorter |
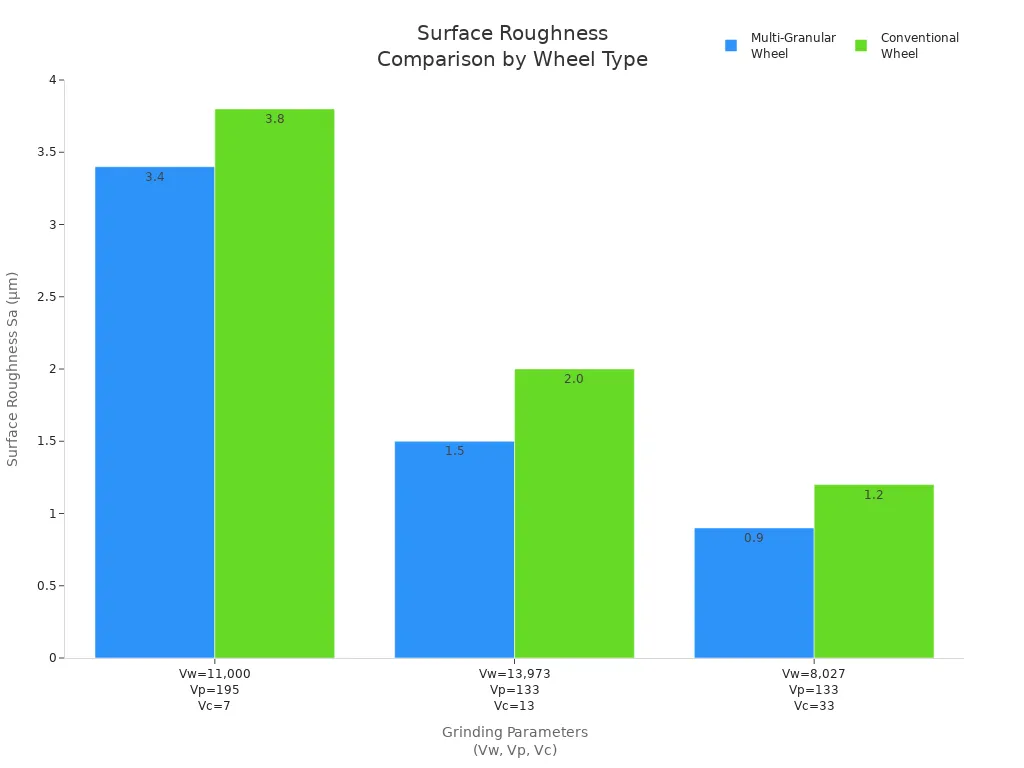
Picking the right wheel helps you do your job better. It also makes the wheel last longer for each use.
FAQ
What materials work best with metal bond grinding wheels?
Metal bond grinding wheels work best on hard and brittle things. These include tungsten carbide, ceramics, glass, and stone. Many companies use them to shape, finish, and polish these tough surfaces.
How often should operators dress metal bond grinding wheels?
Operators should dress the wheel when it stops working well or gets shiny. Checking the wheel often helps keep it sharp and accurate. How often you dress the wheel depends on the job, the material, and the wheel type.
Can metal bond grinding wheels be used for wet and dry grinding?
Yes, you can use metal bond grinding wheels for both wet and dry grinding. Wet grinding helps keep heat and dust down. Most shops like wet grinding because it makes the wheel last longer and gives a better finish.
Why do metal bond wheels cost more than resin or vitrified wheels?
Metal bond wheels cost more because they use pricey materials like diamond or CBN and metal powders. Making these wheels also uses more energy. These things make them cost more than resin or vitrified wheels.
What safety precautions should users follow with metal bond grinding wheels?
Operators must wear safety goggles, gloves, and hearing protection. They should check the wheel for cracks before using it. The wheel must be put on and balanced the right way to stop accidents. Always follow the safety rules from the manufacturer.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools

