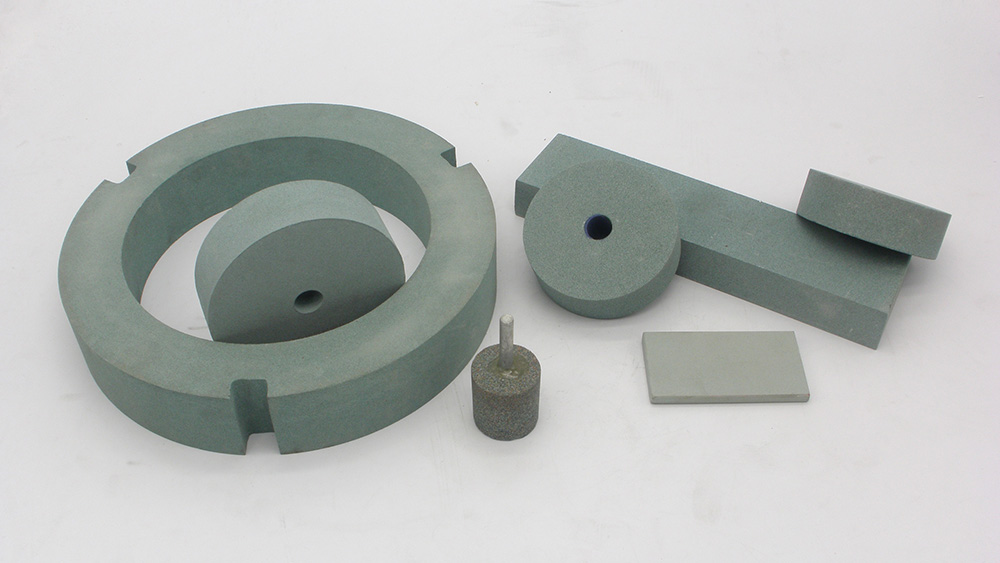
Choosing the right carborundum grinding wheel for your project makes all the difference. You want a wheel that matches your work material, whether you’re working on stone, glass, or metal. Think about the material type, its hardness, the right grit size, and the bond that holds everything together. When selecting a grinding wheel, always check the wheel’s size and if it fits your machine. Paying attention to these details helps you get smoother grinding, boosts performance, and keeps you safe.
Tip: The best results come when you match the wheel’s grit and structure to your job—coarse grit for fast removal, fine grit for a smooth finish.
Key Takeaways
Make sure your grinding wheel’s abrasive type and hardness match the material you are working on. This helps you get better results and makes the wheel last longer.
Pick the right grit size. Coarse grit takes off material quickly. Fine grit makes the surface smooth. Very fine grit is good for polishing.
Choose the correct bond type. Use vitrified bonds for tough jobs. Use resin bonds for smoother finishes and easier shaping.
Always check if the wheel’s size and shape fit your grinder. This keeps you safe and helps you grind well.
Take care of your grinding wheel. Dress it often. Look for any damage. Use coolant when needed. Store it in a dry place.
Work Material
Material Type
When you choose a carborundum grinding wheel, think about what you will grind. Different materials need different abrasive grains and wheel materials. If you are grinding hard metals or glass, pick a wheel with sharp and strong abrasive grains. Softer metals need another kind of abrasive. Here is a table that shows some common materials and where they are used:
Material Type | Characteristics and Uses | Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|
Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Very hard, conducts heat well, has sharp edges | Used for grinding hard metals, ceramics, stone, glass, and non-ferrous metals |
Aluminum Oxide | Good for many jobs, not expensive | Used in general metalworking and finishing |
Ceramic Bonded Wheels | Great for precise grinding, lasts a long time | Used in aerospace and car part grinding |
Diamond Wheels | Super hard, gives high precision | Used for grinding ceramics, carbide, and very hard things |
You can find these abrasive grains in many places, like metal shops, car factories, and building sites. Every job needs the right wheel material to work best. If you use the wrong wheel, it can fill up too fast or wear out quickly.
Material Hardness
How hard your material is matters a lot when picking a grinding wheel. Harder materials need stronger abrasive grains. Softer materials can use less tough abrasives. If you do not match the wheel to your material’s hardness, you can have problems. Here are some mistakes people make:
Using a wheel that needs more pressure than your machine can give. This makes the abrasive grains wear out fast.
Picking a grit size that is too fine. This slows down your grinding and gives a bad finish.
Not matching the wheel hardness to your work material. This makes the wheel not work well.
Forgetting the type of grinding you are doing. Rough work and finishing need different wheels.
Choosing a wheel that fills up fast, especially with aluminum.
Tip: Always check how hard your work material is before you start. This helps you pick the right abrasive grains and saves you time and trouble.
Carborundum Grinding Wheel Types

When you look at carborundum grinding wheel types, you will see many shapes and designs. Each type works best for certain jobs. If you want to get the most out of your grinding, you need to know which wheel fits your needs.
Abrasive Options
Choosing abrasive wheels is a big step in getting the right finish. You have several abrasive options, and each one has its own strengths. Here’s a quick look at the main types:
Abrasive Type | Suitable Materials | Key Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum Oxide | Metals under 50 Rockwell C | Good for steel and stainless steel; works for many grinding jobs; affordable and easy to find. |
Silicon Carbide | Hard alloys, soft metals, glass, ceramics | Great for non-ferrous metals and brittle materials; keeps cutting edge sharp; resists clogging. |
Diamond | Hardened steels, ceramics, tungsten carbide | Super tough; removes material fast; perfect for finishing hard coatings and mixed materials. |
When you are choosing abrasive wheels, think about what you will grind. Silicon carbide wheels work well on non-ferrous metals, glass, and stone. They handle hard or brittle materials without clogging. If you need to grind very hard things, like ceramics or carbide, diamond wheels are a smart choice. Aluminum oxide wheels are good for most steel jobs.
Tip: Always match the abrasive to your work material. This helps you get better results and keeps your grinding wheel from wearing out too fast.
Application Fit
You will find many shapes and types of carborundum grinding wheels. Each one fits a different job. Here’s a table to help you see the main types:
Grinding Wheel Type | Description |
|---|---|
Straight Grinding Wheels | Most common; used for surface and cylindrical grinding. |
Cylinder or Wheel Ring | Wide surface; best for flat surfaces on large grinders. |
Tapered Grinding Wheels | Stronger edge; good for gear teeth and thread grinding. |
Straight Cup | Cup shape; extra surface for tool and cutter grinding. |
Dish Cup | Thin cup; fits into slots and crevices. |
Saucer Grinding Wheels | Special shape; used for twist drills and saw blade care. |
Diamond Grinding Wheels | Industrial diamonds; best for concrete, gemstones, and very hard materials. |
When you pick a grinding wheel, think about your project. Straight wheels work for most jobs. Cup and dish wheels help with tricky shapes or tight spots. Diamond wheels are best for tough jobs or mixed materials.
Keep safety in mind. Grinding wheels can make dust that is not safe to breathe. Some wheels, like resin-bonded types, can give off fumes. Always wear eye and face protection. Use good ventilation and check your wheels for cracks or damage before you start.
Note: Store your abrasive wheels in a dry place. Wet or hot conditions can weaken them and make them unsafe.
Grit Size Selection
Choosing the right grit size makes a big difference in how your grinding wheel performs. You want to match the grit to your project for the best results. Let’s break down what you need to know.
Coarse vs. Fine
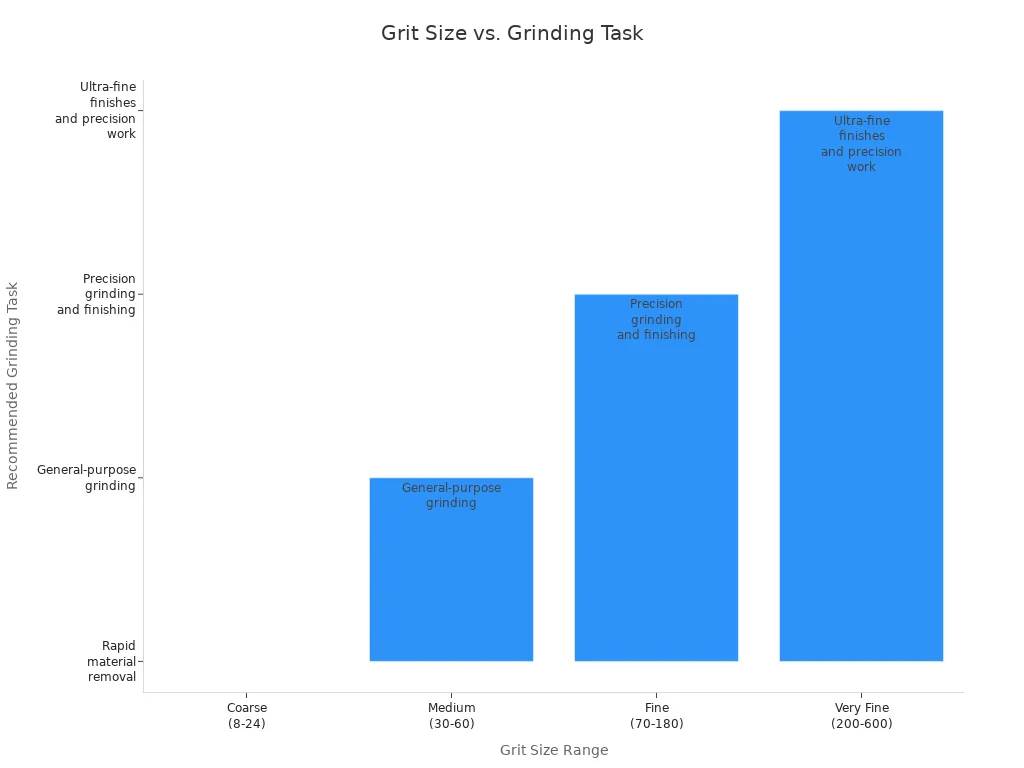
When you look at grit size, you’ll see numbers like 24, 60, or even 220. Lower numbers mean a coarser grit, while higher numbers mean a finer grit. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
Grit Size Range | Recommended Grinding Task | Typical Application / Material |
|---|---|---|
Coarse (8-24) | Rapid material removal | Rough grinding where finish is not a priority |
Medium (30-60) | General-purpose grinding | Balances removal rate and surface finish |
Fine (70-180) | Precision grinding and finishing | Provides fine surface finish |
Very Fine (200-600) | Ultra-fine finishes and precision | Surface finishing for high-quality finish |
If you need to remove a lot of material fast, pick a coarse grit. These wheels work great for shaping or cleaning up rough surfaces. Fine grit wheels, on the other hand, help you get a smooth finish. They work slower but leave fewer scratches.
Tip: Coarse grit wheels cut faster but leave a rougher surface. Fine grit wheels take longer but give you a smoother result.
Finish Quality
You want your project to look good and feel smooth. The grit size you choose affects the finish quality. Here’s what you can expect:
Coarse grits (24 to 36) remove material quickly but leave a rough finish.
Medium grits (46 to 60) give you a balance between speed and smoothness.
Fine grits (80 to 120) are perfect for sharpening tools or finishing parts with a smooth touch.
Super fine grits (150 to 600) polish surfaces until they shine.
Hard materials like ceramics or hardened steel need finer grits to avoid cracks or chips. Softer metals, such as aluminum, can handle coarser wheels without damage. Fine grit grinding can even make surfaces as smooth as glass, especially on tough materials.
Note: Always match your grit size to your project’s needs. You’ll get better results and make your grinding wheels last longer.
Bond & Grade
Bond Types
When you pick carborundum wheels, you need to look at the bond type. The bond holds the abrasive grains together and shapes how the wheel works. You will find two main types: vitrified and resin bonds. Each one has its own strengths and best uses.
Bond Type | Key Characteristics | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
Vitrified Bond | Glass-like, rigid, heat resistant | High precision, great for heavy-duty jobs, stable | Brittle, needs careful handling |
Resin Bond | Flexible, absorbs vibration, easy to shape | Smoother finishes, less heat, easy to dress | Not for high heat, less tough for big jobs |
Vitrified bonds give you a strong and stable grinding wheel. You can use these for tough jobs like metal fabrication or tool making. They handle heat well but can break if you drop them. Resin bonds make wheels that are flexible and smooth. These work well for shaping and finishing, and they help reduce heat. You can dress and shape resin wheels more easily, but they do not like high temperatures.
Tip: Always match the bond type to your project. If you need heavy-duty grinding, go with vitrified. For smoother finishes or tricky shapes, resin wheels are your friend.
Wheel Hardness
Wheel hardness tells you how well the wheel holds onto its abrasive grains. You will see a code on the wheel, like “P,” that shows its hardness. This matters because it changes how fast you can grind and how long your wheels last.
Hard wheels, like silicon carbide, keep their sharp edges longer. You can grind faster and finish jobs quicker.
These wheels last longer and do not wear out as fast, so you save money.
Hardness helps the wheel stay sharp, even after lots of use.
Good thermal conductivity in hard wheels helps move heat away, so your tools stay safe.
If you match the hardness to your job, you get better grinding and less tool wear.
If you work with hard materials, pick a harder wheel. For softer materials, a softer wheel works better. Always check the hardness code before you start. This helps you get the best results and keeps your grinding wheel in good shape.
Note: Using the right wheel hardness means less downtime and smoother grinding every time.
Grinder Wheels: Size & Shape
Tool Compatibility
When you pick grinder wheels, you need to make sure they fit your grinder. Not every wheel works with every machine. Each grinder has its own size and shape limits. If you use the wrong wheel, it might not fit or could even break during use.
Flat wheels work best for surface grinding jobs.
Cylindrical wheels help you grind round surfaces.
Cup or dish wheels are great for edges or concave shapes.
Your grinder will only accept certain wheel sizes. Always check your machine’s manual before you buy new grinder wheels. Some wheels, like quick change types, make swapping fast and easy. These smaller wheels boost productivity and let you switch tasks without tools. You also need to match the wheel’s thickness and diameter to your grinder’s holder pad or spindle. If you skip this step, you risk damaging your machine or hurting yourself.
Tip: Always double-check the wheel size and shape before you start. This keeps your grinder running safely and smoothly.
Project Needs
Every project needs a different approach. The size and shape of your grinder wheels should match your job. For heavy material removal, pick a thicker, larger wheel. If you need to polish or finish, choose a thinner, softer wheel. Some wheels, like the Standard Abrasives™ Silicon Carbide HD Unitized Wheels, come in sizes from 1 to 12 inches. You can find wheels for cleaning, deburring, blending, or polishing.
Here’s a quick table to help you match wheel size and shape to your project:
Project Type | Best Wheel Size & Shape | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
Heavy Grinding | Large, thick flat wheels | Removes more material, lasts longer |
Fine Finishing | Small, thin, soft wheels | Gives a smooth, polished finish |
Edge Work | Cup or dish wheels | Reaches tight spots and corners |
Quick Changes | Small, quick change wheels | Saves time, easy to swap |
You want your grinder wheels to last and give you the best results. Pick the right size and shape for your project, and you’ll work faster and safer.
Machine Compatibility
Speed & Power
You want your grinder to work smoothly with your carborundum grinding wheel. Always check your machine’s speed and power before you start. Each grinding wheel has a maximum RPM, which tells you how fast it can spin safely. For example, a 6-inch fine grinding wheel might have a top speed of 4,140 RPM. If your grinder spins faster than this, the wheel could break or even fly apart. That’s dangerous! Always match your grinder’s speed to the wheel’s rating.
Power matters, too. A strong grinder can handle bigger, thicker wheels and tougher jobs. If your grinder is too weak, it might slow down or stall when you push hard. This can make your work take longer and wear out your wheel faster. Look at your grinder’s horsepower and make sure it fits the job you want to do.
Safety Checks
Before you use a new grinding wheel, take a minute to check if it fits your grinder. You want everything to line up just right. Here’s a handy table to help you see what to look for:
Required Value / Feature | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
Wheel Diameter | 9 inches (228.6 mm) | Your grinder must fit this size for safe use. |
Wheel Thickness | 6 mm | Makes sure the wheel is stiff but not too stiff for your grinder. |
Wheel Width | 16 mm | Affects how much you can grind at once. |
Maximum RPM | At least 15,250 RPM | Never use a grinder that spins faster than the wheel’s limit. |
Maximum Speed | Up to 80 m/s | Stay within this speed for safety. |
Load Capacity | Minimum 1,200 kgf | Your grinder should support heavy-duty work. |
Wheel Shape | Depressed Center Disk | Make sure your grinder can hold this shape. |
Safety Features | Reinforced Rim | Use grinders that work with reinforced wheels to lower breakage risk. |
Certification | ISO 9002 | Pick grinders and wheels that meet safety standards. |
Don’t forget about coolant. Some grinders use coolant to keep things cool and stop sparks. This helps your wheel last longer and keeps you safe. Always check for cracks or damage before you mount a wheel. If you see anything wrong, don’t use it. Safety comes first!
Tip: Always follow your grinder’s manual and use the right wheel for your machine. This keeps you safe and helps your projects turn out great.
Better Grinder Wheel Performance
Optimizing Settings
You want your grinding wheel to work its best every time. Start by picking the right wheel for your job. For non-ferrous metals or carbide, use a silicon carbide abrasive wheel. Make sure the wheel fits snugly on the arbor. If it feels loose, use a bushing to get a perfect fit. Tighten the arbor nut just enough—too tight can crack the wheel.
The angle you use matters, too. If you use a Type 27 wheel, hold it at a 25 to 30-degree angle. This helps you grind faster and keeps the wheel from wearing out unevenly. Always use smooth, steady strokes. Pressing too hard or using the wrong angle can cause problems like uneven wear or even wheel breakage.
Here’s a quick table to help you set up for better grinder wheel performance:
Setting | What To Do |
|---|---|
Wheel Type | Match to your material and job |
Mounting | Fit wheel snugly, use bushings if needed |
Tightening | Snug fit, not too tight |
Operating Angle | 25-30° for Type 27 wheels |
Pressure | Use steady, light pressure |
Tip: Always check your grinder’s speed and never go over the wheel’s max RPM.
Maintenance Tips
Keeping your grinding wheel in top shape helps you get the best results for both grinding and sharpening. Dress your wheel often with a dressing tool. This removes any material stuck to the wheel and exposes fresh, sharp grains. If you skip this step, the wheel can get clogged and stop cutting well.
Watch out for common problems like uneven wear or wheel loading. These happen when you use too much pressure, grind at the wrong angle, or don’t mount the wheel right. If you see material sticking to the wheel, increase the coolant flow or switch to a softer bond wheel.
Here are some easy maintenance tips:
Dress the wheel regularly to keep it sharp.
Check for cracks or damage before each use.
Make sure the wheel is balanced and mounted correctly.
Use enough coolant to keep things cool and prevent material from sticking.
Store wheels in a dry, safe place.
If you follow these steps, you will get smoother grinding and sharpening, and your wheels will last longer.
You’ve learned the seven key tips for picking the best carborundum grinding wheel. When you match the wheel to your material, check grit size, bond, and machine fit, you boost both safety and results. Here’s a quick checklist to keep in mind:
Choose wheels with reinforced backing and the right abrasive for your job.
Always use the correct RPM and safety gear.
Inspect wheels before each use and never use damaged ones.
Careful selection pays off. Take a look at how your choices impact tool life and efficiency:
Specification | Impact on Tool Life and Efficiency |
|---|---|
Hard wheels last longer and give a better finish. | |
Maximum RPM | Right speed keeps wheels safe and working longer. |
Grain Size | Finer grains give smoother finishes. |
Pick wisely, and your grinder will work better, safer, and last longer!
FAQ
What is a carborundum grinding wheel used for?
You use a carborundum grinding wheel to shape, sharpen, or smooth metal, stone, glass, or ceramics. It works well for removing rough edges, cleaning surfaces, or preparing parts for finishing.
How do I know which grit size to pick?
Think about your project. Use coarse grit for fast material removal. Pick fine grit for a smooth finish. Check the grit number on the wheel. Lower numbers mean coarser grit.
Can I use any grinding wheel on my machine?
No, you need to match the wheel size and speed rating to your grinder. Always check your machine’s manual. Using the wrong wheel can damage your grinder or cause injury.
How do I keep my grinding wheel in good shape?
Dress your wheel often with a dressing tool. Store it in a dry place. Check for cracks before each use. Use enough coolant if your grinder allows it.
What safety gear should I wear when grinding?
Wear safety glasses or a face shield. Use gloves and hearing protection. A dust mask helps if you work with stone or glass. Always follow your grinder’s safety rules.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools

