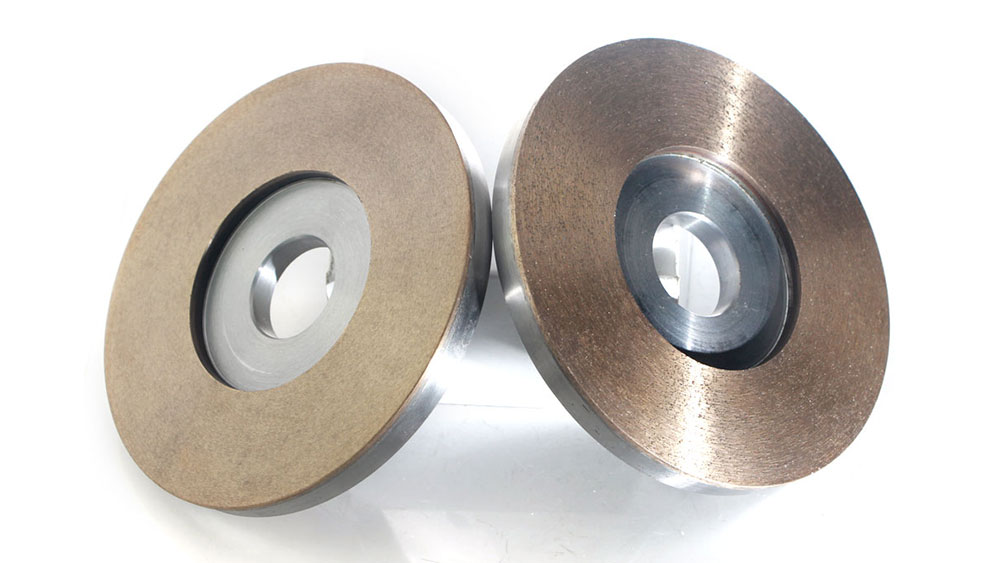
A surface grinding wheel helps make flat surfaces smooth and even. It takes off a little bit of material at a time. This tool gives parts a nice, smooth finish. Many industries use surface grinding to get very exact shapes. They also use it to make surfaces look good. In 2023, the world market for surface grinding wheels was about $3.5 billion. Experts think this number will keep growing. This is because more people want very precise parts in cars, planes, and electronics. Picking the right surface grinding wheel keeps workers safe. It also shows why these wheels are important in factories today.
Key Takeaways
Surface grinding wheels have many types like straight, cylinder, tapered, cup, and diamond wheels. Each type works best for certain jobs and materials.
Picking the right wheel depends on the workpiece material. It also depends on if you want roughing or finishing. Grit size, bond type, and machine fit are important too.
You must mount, balance, and dress the wheels the right way. Using coolant helps keep wheels safe, sharp, and lasting longer. This also makes the finish look better.
Surface grinding wheels are important in many industries. These include automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical fields. They help make parts smooth and exact.
New technology brings smart wheels with sensors. There are also eco-friendly abrasives. These make grinding safer, faster, and better for the planet.
Types of Surface Grinding Wheels
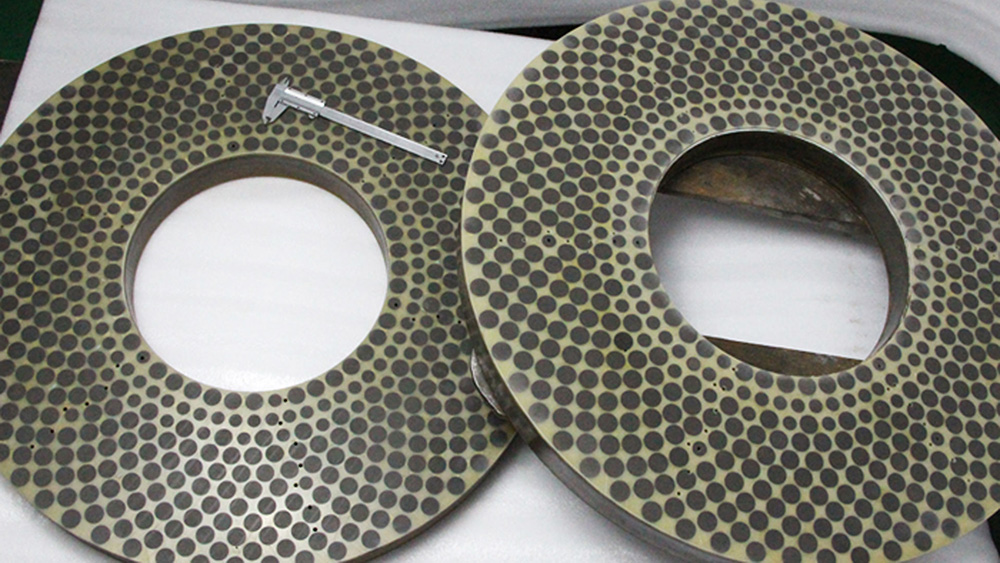

Surface grinding wheels have many shapes and are made from different materials. Each kind is best for certain jobs. The main types are straight wheels, cylinder wheels, tapered and cup wheels, and diamond grinding wheels. These wheels use special bonds and abrasive materials for each task.
Straight Wheels
Straight wheels are the most used surface grinding wheel. They are flat and shaped like a disc. Factories use them to make flat surfaces smooth and to sharpen tools. Straight grinding wheels work on steel, ceramics, and carbide. Workers like them because they are simple and come in many sizes.
Tip: Straight wheels, or Type 1 wheels, are good for most grinding and sharpening. They make flat surfaces smooth.
Wheel Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
Straight Wheel | Flat, disc-shaped abrasive | Flat surface grinding, tool sharpening |
Type 1 | Flat surface, no center depression | General grinding, sharpening tools |
Depressed center for angled access | Deburring, surface prep, heavy stock removal |
Straight wheels use different abrasive grains. Aluminum oxide is for metals. Silicon carbide is for softer materials. They come in many grit sizes. Coarse grits remove material fast. Fine grits make smooth finishes. Straight wheels are toolroom wheel types and are found in many workshops.
Cylinder Wheels
Cylinder wheels are round and look like barrels. They are not as common as straight wheels but are important for grinding round things. Factories use cylinder wheels to grind rollers, shafts, and pipes. The wheel spins along the workpiece, which is good for round surfaces.
Cylinder wheels have a more open design. This helps remove chips and keeps the wheel cool during long jobs. Workers use cylinder wheels to shape or smooth round parts.
Tapered and Cup Wheels
Tapered wheels are shaped like a cone and are thick at one end. Cup wheels look like a shallow bowl or cup. Both types help grind places that straight wheels cannot reach. Tapered wheels are good for corners or edges. Cup wheels are used on vertical spindle grinders, where the side of the wheel does most of the work.
Note: Cup wheels can take off a lot of material fast. They are used for big flat plates in car and machine shops.
Cup wheels and tapered wheels use different abrasive materials and bonds. Some use vitrified bonds for strength. Others use resin bonds for a smoother finish. These wheels help workers grind tools, shape parts, and get surfaces ready for finishing.
Diamond Grinding Wheel
Diamond grinding wheels are superabrasive grinding wheels. They use synthetic diamond as the abrasive. This makes them very hard and long-lasting. Workers use diamond grinding wheels to grind very hard things like carbide, ceramics, and glass.
Diamond grinding wheels are very hard and last a long time.
They make less heat, which protects the wheel and the workpiece.
Diamond grinding wheels can do high-precision jobs and remove material fast.
They are used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Diamond grinding wheels come in shapes like straight, cup, or dish. The bond type—resin, metal, or vitrified—changes how the wheel works. These wheels are best for grinding hard, brittle, or heat-sensitive materials.
Did you know? Diamond grinding wheels do not make dangerous dust and are built strong, so they are safe for many grinding jobs.
Main Types by Shape, Bond, and Abrasive
Shapes: Straight, cylinder, tapered, cup, dish, and saucer wheels.
Bond Types: Vitrified (strong and stiff), resin (soaks up vibration), metal (for diamond wheels), silicate, shellac, and rubber.
Abrasive Materials: Aluminum oxide (for steel), silicon carbide (for non-ferrous metals), diamond (for hard materials), CBN (for hardened steels).
Type 1 vs. Type 27 Wheels
Feature | Type 1 Grinding Wheel (Straight) | Type 27 Grinding Wheel (Depressed Center) |
|---|---|---|
Design | Flat surface, no center depression | Recessed middle for angled access |
Typical Use | General grinding, sharpening | Deburring, surface prep, heavy stock removal |
Operation Angle | Used flat on the surface | Allows angled operation, fits tight spaces |
Common Materials | Aluminum oxide, silicon carbide | Aluminum oxide, ceramic, silicon carbide |
Type 1 wheels are flat and used for most surface grinding. Type 27 wheels have a depressed center, so they are better for grinding at angles or in small spaces.
Picking the right surface grinding wheel depends on the job, the material, and the finish you want. Knowing the types of surface grinding wheels helps workers choose the best tool for each job.
Surface Grinding Wheel Composition
Abrasive Materials
Surface grinding wheels use different abrasive materials for each job. Each material has its own special features:
Aluminum oxide is good for grinding ferrous metals and strong steels. It has grains that sharpen themselves, so it lasts longer.
Silicon carbide works best on soft metals like aluminum, bronze, and brass. It also grinds stone, marble, and glass. This abrasive is very sharp but breaks easily, so it wears out faster.
Ceramic aluminum oxide is very strong and hard. It grinds tough metals like titanium and stainless steel. This abrasive stays sharp because it breaks into small pieces as you use it.
Diamond grinding wheel types use diamond as the abrasive. These wheels cut very hard things like carbide and ceramics. They are very accurate and last a long time.
Bond Types
The bond keeps the abrasive grains together. Different bonds change how the wheel works and how long it lasts. Here is a table that shows common bond types and what they do:
Bond Type | Performance Characteristics | Durability Characteristics | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Flexible, makes a smooth finish, uses less force | Sensitive to heat, does not last long under stress | Needs coolant for best results | |
Metal bond diamond wheels | Wears down slowly, keeps its shape for a long time | Lasts a long time, good for hard jobs | Hard to fix, costs more |
Vitrified bond diamond wheels | Strong, stiff, stays stable at high heat | Durable, accurate, keeps its size and shape | Brittle, best for very careful work |
Hybrid and vacuum brazed | Mix of resin and metal, or strong heat-resistant bonds | Lasts a long time, works well in tough jobs | Needs special machines and care |
Picking the right bond type helps the diamond grinding wheel work better and last longer.
Grit Size and Structure
Grit size means how big the abrasive grains are. Structure tells how close the grains are packed together. Both change how the wheel grinds:
Coarse grits take off material fast but leave a rough surface.
Fine grits make smoother surfaces but remove less material.
Medium grits are a mix of speed and smoothness.
Wheels with open structure clear chips better and stay cool.
Dense structure gives a smoother finish but can clog up faster.
Choosing the right grit size and structure helps control how smooth the finish is and how long the grinding wheel lasts.
Selection Guide for Types of Grinding Wheels
Picking the right grinding wheel is very important. It keeps grinding safe and helps get good results. This guide shows how to pick the best surface grinding wheel. You need to think about what the workpiece is made of. You also need to know what kind of grinding you will do. The machine’s features matter too.
Workpiece Material Compatibility
First, match the surface grinding wheel to the workpiece material. Every material needs a certain abrasive type and wheel hardness.
Aluminum oxide wheels are good for ferrous metals like steel.
Silicon carbide wheels work best for non-ferrous metals and cast iron.
CBN wheels are used for hardened steels and can handle heat.
Diamond wheels grind hard things like carbide, ceramics, and glass.
The workpiece’s hardness changes which wheel grade you need. Harder materials need a softer wheel grade to stay sharp. Softer materials use harder wheel grades so the wheel lasts longer. The bond type is important too. Vitrified bonds are strong and last a long time. Resin bonds soak up vibration and help make smooth finishes.
Tip: Using the right grinding wheel for the workpiece makes grinding better. It gives a nicer finish and helps the wheel last longer.
Grinding pressure and contact area also matter. High pressure needs stronger grains and bigger grits. Small contact areas need harder grades. Large areas can use softer grades. Coolant helps lower heat and friction. This makes grinding better.
Operation Type: Roughing vs. Finishing
Grinding changes based on the job. Roughing takes off material fast. Finishing makes the surface smooth and very exact.
For roughing, pick a coarse grit size and a softer bond. This setup removes more material but leaves the surface rough.
For finishing, use a fine grit size and a harder bond. This makes the surface smooth and more accurate.
The finish you want helps you pick the grit size and bond. Coarse grits work fast but leave marks. Fine grits take longer but make the surface smooth. The right bond keeps the wheel steady while grinding.
Operation Type | Grit Size | Bond Type | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Roughing | 24-46 | Softer | Fast removal, rougher |
Finishing | 60-120+ | Harder | Smooth, precise finish |
Grinding also depends on the contact area. Small areas need stronger grains. Big areas can use softer grains. Changing these things helps get the best results.
Machine and Wheel Specifications
The grinding machine must fit the wheel’s needs. Wheel size, speed, and how it mounts should match the machine.
Always check the wheel’s speed rating. Never use a wheel that is not made for your machine’s speed.
The wheel’s core material changes its weight. Lighter cores like carbon fiber or aluminum make big wheels easier to use.
The way you mount the wheel must fit the machine for safety and good work.
The machine’s horsepower helps pick the wheel grade. Strong machines can use harder grades and tough grains. Weaker machines need softer grades and grains that break easily.
Note: Using the right wheel for the machine stops accidents. It also helps the grinding go well.
Step-by-Step Guide for Choosing the Right Surface Grinding Wheel
Find out what the workpiece is made of and how hard it is.
Choose if you are roughing or finishing.
Check the machine’s wheel size, speed, and mounting.
Think about using coolant and how much pressure you will use.
Ask grinding experts for help with special jobs.
Matching Grit Size, Bond, and Wheel Shape
Criterion | Description | Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
Abrasive Type | What the abrasive grains are made of (like aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, CBN, diamond) | Shows if it works for the material you are grinding |
Grit Size | How big the abrasive pieces are; bigger for rough, smaller for smooth | Changes how smooth the finish is and how fast it grinds |
Grade (Bond Strength) | How strong the bond is; softer for fast cuts, harder for careful work | Changes how hard the wheel is and how it cuts |
Structure | How close the abrasive grains are; helps coolant flow and chip removal | Changes how well it cuts and how smooth the finish is |
Bond Type | What holds the grains together (vitrified, resin, metal, hybrid) | Changes how flexible, heat-resistant, and tough it is |
Wheel Shape | The shape made for certain grinding jobs | Must fit the job and the machine |
Choosing the right surface grinding wheel takes planning. You need to balance how fast you remove material, how long the wheel lasts, and the cost. Superabrasive wheels cost more at first but can save money later. Working with grinding experts helps you pick the best wheel and machine for each job.
Applications of Surface Grinding Wheels
Industrial and Material-Specific Uses
Surface grinding wheels are used in many factories and shops. Workers pick different wheels for each job. The wheel they use depends on the material they need to grind or finish. Each abrasive type works best with certain materials and tasks. The table below shows which abrasive is good for each job:
Abrasive Type | Common Industrial Applications by Material Type |
|---|---|
Aluminum Oxide | Used for carbon steel, alloy steel, wrought iron, and bronze. Versatile abrasive for various steels. |
Silicon Carbide | Suitable for non-ferrous materials such as rubber, stone, plastic, glass, cast iron, soft bronze, and aluminum. |
Zirconia Alumina | Durable abrasive ideal for steel and steel alloys, often used in cut-off applications. |
Ceramic Aluminum Oxide | Modern, self-sharpening abrasive used for precision grinding on difficult steels and alloys. |
Grinding wheels are used for fine grinding of carbide tools. They also polish glass and ceramic materials. Some wheels grind composite materials. Special wheels are used to grind concrete floors flat and smooth. These jobs help make parts that fit well and last longer.
Workers pick the right abrasive for each job. This helps them get good results and keeps the workpiece safe.
Surface Grinding in Key Industries
Many industries need surface grinding every day. Factories use grinding wheels to shape and smooth parts for many products. The table below lists some big industries and how they use grinding wheels:
Industry | Specific Processes Using Surface Grinding Wheels |
|---|---|
Automotive | Grinding engine parts, transmission components, brake rotors, cylinder heads for precise dimensions and smooth finishes |
Aerospace | Grinding turbine blades, aircraft engine parts, landing gear components requiring high precision and quality |
Electronics | Grinding printed circuit boards, semiconductor wafers, connectors to achieve smooth, flat surfaces |
Medical | Grinding medical devices, implants, surgical instruments to ensure precise dimensions and smooth surfaces |
Tool and Die Making | Grinding precision cutting tools, molds, and dies for accuracy and quality |
In car factories, workers grind engine and brake parts. This helps engines and brakes work well. In aerospace, workers grind turbine blades and landing gear. These parts must be very exact. Electronics makers grind circuit boards to make them flat and smooth. Medical workers grind implants and tools so they are safe and smooth. Tool and die shops grind molds and dies to get the right shape.
Surface grinding is important in all these jobs. It helps make strong, safe, and high-quality products.
Best Practices and Safety
Mounting and Balancing
Proper mounting and balancing help surface grinding wheels work safely and last longer. Workers should always clean the flanges, arbor, and wheel hub before installation. Even small bits of dirt or oil can cause imbalance. Flanges must match the wheel size and type. Before mounting, a ring test checks for cracks. A clear ringing sound means the wheel is safe. Workers should tighten bolts in a star pattern and use the correct torque. This prevents the wheel from warping. Balancing the wheel is important. Workers can use a balancing arbor to find the heavy spot and add weights until the wheel spins evenly. For high-precision jobs, a dynamic balancer with sensors gives the best results. After dressing the wheel, workers should check the balance again. Keeping a maintenance log helps track installation dates and wheel details.
Coolant and Dressing
Coolant keeps the grinding wheel and workpiece cool. It reduces heat, which helps the wheel keep its shape and improves durability. Workers should check coolant levels and flow before starting. Dressing the wheel removes dull grains and keeps the wheel sharp. A diamond dresser works well for this job. Dressing also helps the wheel stay balanced and gives a better finish. After dressing, the wheel may need rebalancing. Clean coolant and regular dressing help answer the question, “how long does a grinding wheel last?” A well-maintained wheel lasts longer and works better.
Safety Checks and PPE
Safety checks protect workers and equipment. Before grinding, workers should inspect the wheel for cracks, chips, or wear. Guards must be in place and secure. Electrical cords and plugs need checking for damage. Workpieces must be clamped tightly. Workers should stand to the side when starting the grinder. Let the wheel run for one minute to check for problems. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a must. Workers should wear safety glasses with side shields, face shields, gloves, and hearing protection. A clean, dry storage area keeps wheels safe when not in use. Following these steps helps prevent accidents and keeps grinding safe.
Innovations in Surface Grinding Wheels
Advanced Bonds and Smart Wheels
Surface grinding wheels have changed a lot lately. New bonds help wheels work better and last longer. Some wheels now use nano-crystalline ceramic grains. These grains make the wheel stronger and more efficient. Norton Quantum™ Prime wheels use this new technology. They help workers grind faster and keep the wheel’s shape. They also stop the workpiece from burning.
Metal bond wheels are better now too. Makers mix powdered metals with superabrasives like diamond or CBN. This makes a hard, tough wheel that needs less dressing. It also works well with coolant. Factories can make these wheels for special jobs. This means tools last longer and there is less downtime.
Hybrid bond wheels mix the best parts of resin and metal bonds. Some companies use 3D printing to make these wheels. This lets them control the wheel’s shape and grain mix. Tests show hybrid wheels last longer and keep their shape. They also need less force to grind.
Smart grinding wheels are a big new step. These wheels have sensors inside them. The sensors watch force, temperature, and wear. They send real-time data to computers. This helps workers and machines change the grinding process right away. Factories use smart wheels with robots and automation. This makes grinding safer and more precise.
Sustainable Abrasives
Sustainability is important in grinding today. Many companies use new materials and methods to help the environment. Some wheels use cubic boron nitride (CBN), which works well and needs less coolant. Others use solid lubricants that are safer and break down naturally.
Self-lubricating wheels help cut down on extra coolants. Factories also use textured wheels that let coolant reach the grinding area better. This lowers heat and saves energy. Some shops use vegetable oils or renewable coolants instead of oil-based fluids.
Recycling helps the planet too. Workers can reclaim alumina from old wheels and use it again. Using less coolant and recycling wheels both lower waste and pollution.
Using sustainable abrasives and smart grinding helps factories save energy, cut emissions, and keep workers safe. These changes make surface grinding better for people and the planet.
Knowing about the different types of surface grinding wheel and how to use them helps workers do careful and high-quality work. Picking the right abrasive, bond, and grit size for each material stops heat damage and makes tools last longer. Checking, dressing, and balancing the wheels often keeps them safe and working well. Learning about new trends in surface grinding helps people use better methods and smart tools. Keeping up with new information leads to better work and safer jobs.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a surface grinding wheel?
A surface grinding wheel helps make flat surfaces smooth and even. It removes small amounts of material to create a precise finish. Many factories use these wheels to shape metal parts and tools.
How often should workers dress a grinding wheel?
Workers should dress the wheel when it becomes dull or glazed. Dressing keeps the wheel sharp and helps it cut better. For best results, check the wheel before each job.
Can one grinding wheel work on all materials?
No, each material needs a specific abrasive. For example, aluminum oxide works on steel, while silicon carbide suits softer metals. Using the right wheel prevents damage and gives a better finish.
Why is balancing a grinding wheel important?
Balancing stops the wheel from vibrating during use. A balanced wheel gives a smoother finish and lasts longer. It also helps keep workers safe.
What safety gear should workers wear when using a surface grinder?
Workers should wear safety glasses, face shields, gloves, and hearing protection. Proper gear protects eyes, hands, and ears from flying debris and loud noise.
Contact Us
For More Grinding Solution or Customized Abrasive Tools

